Cloud Technology Lab v6.0
Question 1
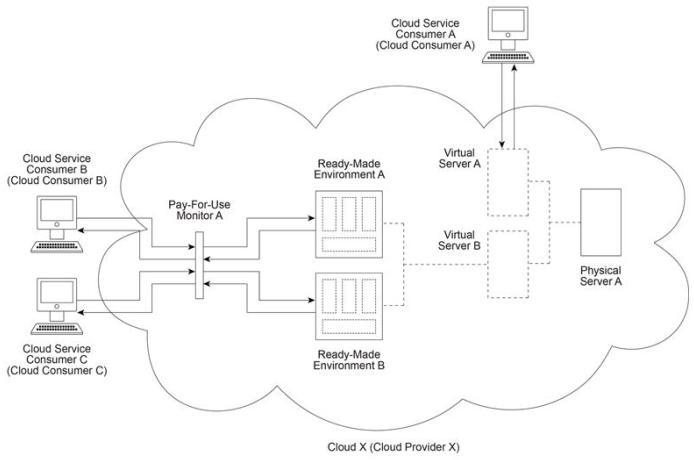
Cloud X (owned by Cloud Provider X) provides Physical Server A which hosts Virtual
Servers A and B. Virtual Server B hosts Ready-Made Environments A and B. Cloud
Service Consumer A uses Virtual Server A as part of an IaaS leasing agreement in which
Cloud Consumer A is charged a fixed monthly fee for unlimited access. Cloud Service
Consumers B and C use Ready-Made Environments A and B respectively as part of a
PaaS leasing agreement based on per-minute usage fees. In both cases, access is monitored via Pay-For-Use Monitor A, which keeps track of log-in and log-out times in order to calculate the usage charges that are billed to Cloud Consumers B and C.
Virtual Server A begins generating a series of exceptions. Soon thereafter, Virtual Server B becomes destabilized, resulting in further exceptions being raised in Ready-Made
Environments A and B. Cloud Service Consumers B and C receive a series of error messages until both of their connections are dropped Finally, Physical Server A shuts down completely. A subsequent investigation reveals that Virtual Server A was the victim of a security attack performed by a malicious cloud service consumer, the attacker generated increased loads of external communication requests on Virtual Server A and the underlying network, causing Physical Server A (along with Virtual Server B) to eventually shut down.
Which of the following statements accurately identifies the type of security threat that corresponds to the described attack - and -provides a solution that can directly mitigate this type of security threat within Cloud X?
- A. Virtual Server A was subjected to a denial of service attack that can be mitigated by implementing the encryption and digital signature mechanisms.
- B. Virtual Server A was subjected to an insufficient authorization attack that can be mitigated by implementing the digital signature and hardened virtual server image mechanisms.
- C. Virtual Server A was subjected to a denial of service attack that can be mitigated by implementing the hardened virtual server image and identity and access management mechanisms.
- D. Virtual Server A was subjected to an insufficient authorization attack that can be mitigated by implementing the single sign-on mechanism.
Answer : C
Question 2
Cloud Provider X (which owns Cloud X) deploys two physical servers (Physical Servers A and B) and two databases (Databases A and B). Virtual Servers A and B are hosted by
Physical Server A and Ready-Made Environments A and B are hosted by Virtual Server B.
Virtual Servers C and D are hosted by Physical Server B. Cloud Service Consumer A regularly accesses Virtual Server D in order to test and deploy a new cloud service that was developed on-premise by the cloud consumer organization operating Cloud Service
- A. The pay-for-use monitor mechanism can be installed to address the requirement for cloud service usage charges to be tracked and recorded. The automated scaling listener mechanism can be implemented to address the requirement for cloud services to be automatically scaled. The multi-device broker mechanism can be implemented to address the requirement for notifications to be issued when cloud service loads exceed thresholds.
- B. The pay-for-use monitor mechanism can be installed to address the requirement for cloud service usage to be tracked and recorded. The automated scaling listener mechanism can be implemented to address both the requirement for cloud services to be automatically scaled and for notifications to be issued when cloud service loads exceed thresholds.
- C. The pay-for-use monitor mechanism can be implemented to address the requirement for cloud service usage charges to be tracked and recorded, for cloud services to be automatically scaled, and for notifications to be issued when cloud service loads exceed thresholds.
- D. The state management database mechanism together with the virtual server mechanism and the automated scaling listener mechanism can be implemented to address the requirement for cloud service usage charges to be tracked and recorded, for cloud services to be automatically scaled, and for notifications to be issued when cloud service loads exceed thresholds.
Answer : B
Question 3
Cloud X (owned by Cloud Provider X) provides Physical Server A which hosts Virtual
Servers A and B. Virtual Server B hosts Ready-Made Environments A and B. Cloud
Service Consumer A uses Virtual Server A as part of an IaaS leasing agreement in which
Cloud Consumer A is charged a fixed monthly fee for unlimited access. Cloud Service
Consumers B and C use Ready-Made Environments A and B respectively as part of a
PaaS leasing agreement based on per-minute usage fees. In both cases, access is monitored via Pay-For-Use Monitor A, which keeps track of log-in and log-out times in order to calculate the usage charges that are billed to Cloud Consumers B and C.
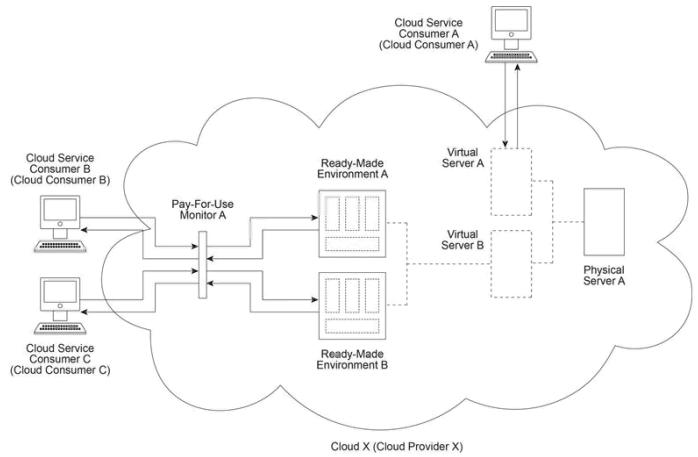
Physical Server A begins to become unstable. Over the course of a 24 hour period, the server shuts down three times, taking down Virtual Servers A and B with it. This causes numerous problems for Cloud Service Consumers A, B and C, which lose connections and encounter a variety of exceptions.
A subsequent investigation of the log files generated by Pay-For-Use Monitor A reveals that the three server crashes coincided with the usage periods of Ready-Made Er n'ronment B b> Cloud Service Consumer B. De 'elopers at the Cloud Consumer 3 organization confirm they did not actually log in during those periods, which leads Cloud
Provider X to discover that another cloud service consumer has been posing as Cloud
Service Consumer B in order to maliciously access Ready-Made Environment B, Virtual
Server B, and Physical Server B on Cloud X. The investigation concludes that the malicious cloud service consumer was able to carry out the attack successfully by obtaining a weak password being used by developers from Cloud Consumer B.
Which of the following statements accurately identifies the type of security threat that corresponds to the described attack - and -provides a solution that can directly mitigate this type of security threat within Cloud X?
- A. Ready-Made Environment B. Virtual Server B and Physical Server B were subjected to a weak authentication attack that can be mitigated by implementing the encryption and digital signature mechanisms.
- B. Ready-Made Environment B. Virtual Server B and Physical Server B were subjected to a malicious intermediary attack that can be mitigated by implementing the cloud-based security groups and hardened virtual server images mechanisms.
- C. Ready-Made Environment B, Virtual Server B and Physical Server B were subjected to a virtualization attack that can be mitigated by implementing the encryption and digital signature mechanisms.
- D. Ready-Made Environments, Virtual Server B and Physical Server B were subjected to an attack that succeeded due to overlapping trust boundaries. This type of attack can be mitigated by implementing the single sign-on mechanism.
Answer : A
Question 4
The cloud service owner of Cloud Service A is evaluating Clouds X, Y and Z to determine which cloud environment can offer the greatest level of reliability. All three clouds are geographically dispersed across three separate time zones. As a result, each cloud experiences usage peaks at different times. Based on the metrics provided, the greater the usage of a cloud, the lower its reliability. When the cloud service owner complains to Cloud
Provider A (the owner of all three clouds) that none of the clouds provide an adequate level of reliability, Cloud Provider A suggests a solution that increases resiliency.
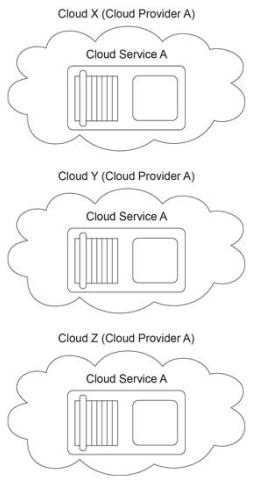
Which of the following statements accurately describes a solution that can be used to fulfill the resiliency requirements of Cloud Service A?
- A. Redundant implementations of Cloud Service A are deployed in all three clouds. The failover system mechanism and a special type of automated scaling listener mechanism are implemented to establish a system whereby one redundant Cloud Service A implementation will automatically take over from another.
- B. A cloud balancing solution is established, whereby an automated scaling listener mechanism is implemented on each cloud in such a way that every cloud can automatically scale out to another cloud. As a result, if reliability problems occur on any one cloud, the subsequent requests will be scaled out to another cloud in a manner that is transparent to cloud service consumers.
- C. A failover system mechanism is implemented on Cloud X, which acts as the primary point of contact for cloud service consumers. Upon failure conditions occurring, the Cloud Service A implementation on Cloud X automatically hands over control of current and future message requests from cloud service consumers to Cloud Y. Cloud Y retains control of cloud service consumer communication until the next failure condition occurs, at which point it hands over control to Cloud Z. Finally, if a failure con
- D. A cloud balancing solution is established, whereby a resource replication mechanism is implemented on each cloud. This allows Cloud Service A to be automatically replicated across cloud environments, thereby enabling each implementation of Cloud Service A to take the place of another, whenever failure conditions occur.
Answer : A
Question 5
Cloud Service Consumer A accesses Cloud Service A (1) that resides in Cloud X. a private
- A. Moving Cloud Service A to Cloud Y will result in the need for Cloud Service A to undergo integration testing to determine how well it can function within Cloud Y and what changes may need to be made to Cloud Service A in order for it to behave as expected. The integration testing and the subsequent changes required for Cloud Service A to function correctly within Cloud Y will incur integration costs that need to be budgeted for.
- B. Because, in this scenario, the cost of capital is comprised of the up-front costs added to the on-going costs, the cost of capital required to move Cloud Service A to Cloud Y will be higher than upgrading Cloud X to accommodate Cloud Service A' s increased usage.
- C. If the existing infrastructure that currently resides in private Cloud X was purchased specifically in support of Cloud Service A, then there may be a financial loss resulting from moving Cloud Service A out of Cloud X. This can be considered sunk costs that need to be evaluated.
- D. By moving Cloud Service A to Cloud Y, there may be a decrease in operational governance control over the Cloud Service A implementation. This can increase locked-in costs because Cloud Consumer A may be forced to form dependencies upon proprietary tools used to configure and maintain the Cloud Service A implementation.
Answer : ACD
Question 6
Cloud Provider X has deployed a virtualization environment in Cloud X comprised of
Physical Server A hosting Virtual Servers A and B. Cloud Provider X implements Cloud
Service A on Virtual Server A and makes it available to Cloud Service Consumer A, which interacts with Cloud Service A by sending and receiving messages (1, 2).
Cloud Provider Y has deployed a virtualization environment comprised of Physical Server B hosting Virtual Servers C and D. Virtual Server C is made available to Cloud Service
Consumer B, which interacts with Virtual Server C (3,4) in order to prepare for the deployment of a new cloud service that will be used internally by Cloud Provider Y to process data obtained from Cloud Service A
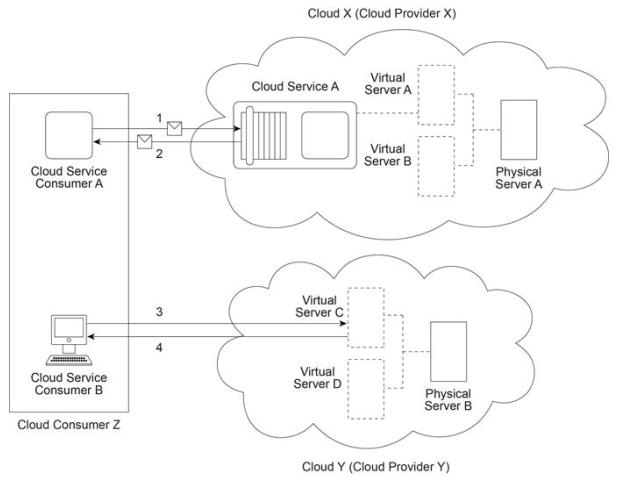
Cloud Consumer Z and Cloud Provider X belong to the same organization. Cloud Provider
Y is a third-party organization. Which of the following statements provides a valid scenario that accurately describes the involvement of cloud deployment models, cloud delivery models, roles and/or boundaries? (Note that the correct answer represents one of multiple valid scenarios that can exist.)
- A. Cloud X is based on the private cloud deployment model. Cloud Service A is based on the SaaS delivery model. Cloud Y is based on the private cloud deployment model. Virtual Server C is being offered as part of the IaaS delivery model. A cloud resource administrator working for Cloud Consumer Z uses Cloud Service Consumer B to access Virtual Server C. Cloud Consumer Z is the cloud service owner of Cloud Service A. Cloud Consumer T s organizational boundary encompasses Cloud Service Consumers A an
- B. Cloud X is based on the private cloud deployment model. Cloud Service A is based on the SaaS delivery model. Cloud Y is based on the community cloud deployment model. Virtual Server C is being offered as part of the IaaS delivery model. A cloud resource administrator working for Cloud Consumer Z uses Cloud Service Consumer A to access Cloud Service A. Cloud Consumer T s organizational and trust boundaries encompass Cloud Service Consumers A and B, Cloud Service A and Virtual Server C.
- C. Cloud X is based on the private cloud deployment model. Cloud Service A is based on the SaaS delivery model. Cloud Y is based on the public cloud deployment model. Virtual Server C is being offered as part of the IaaS delivery model. A cloud resource administrator working for Cloud Consumer Z uses Cloud Service Consumer B to access Virtual Server C. Cloud Consumer Z is the cloud service owner of Cloud Service A. Cloud Consumer Z's organizational boundary encompasses Cloud Service Consumers A and
- D. Cloud X is based on the private cloud deployment model. Cloud Service A is based on the SaaS delivery model. Cloud Y is based on the public cloud deployment model. Virtual Server C is being offered as part of the IaaS delivery model. A cloud resource administrator working for Cloud Consumer Z uses Cloud Service Consumer B to access Virtual Server C. Cloud Consumer Z' s trust boundary encompasses Cloud Service Consumers A and B, Cloud Service A and Virtual Server C. The organization that owns Clo
Answer : D
Question 7
Cloud Consumer A (the organization that owns Cloud Service Consumer A) needs regular access to an external, cloud-based Weather Service that provides up-to-date weather forecast information. Cloud Providers X, Y and Z are competing public cloud providers, each offering a Weather Service with the features required by Cloud Consumer A.
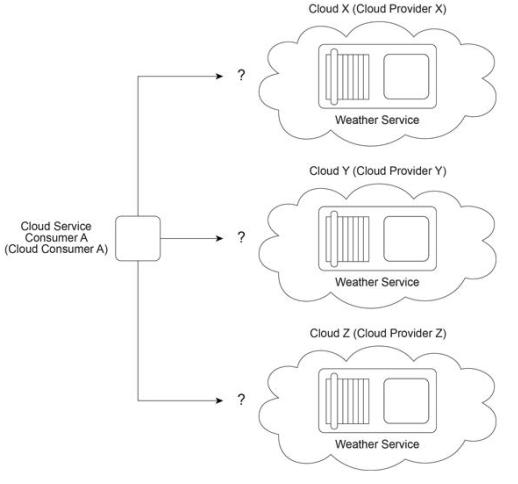
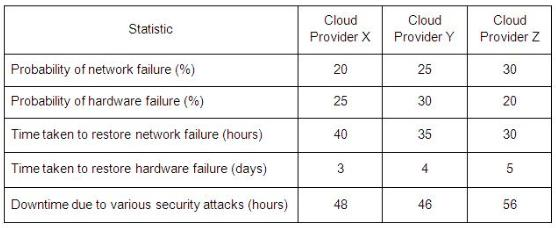
Based on the provided statistics, which cloud provider can offer a Weather Service with the least amount of projected downtime?
- A. Cloud Provider X
- B. Cloud Provider Y
- C. Cloud Provider Z
- D. Any of the three cloud providers, because their availability ratings are identical.
Answer : A
Question 8
Organization A has been expanding and, as a result, is outgrowing the processing capacity of its on-premise Service A implementation. It is determined that this is due to usage
- A. A failover system can be implemented in a hybrid architecture comprised of Organization A's existing on-premise environment and a public cloud environment. The failover system would span both environments so that when Service A is unable to process request messages from Service Consumers A, B or C, the failover system can automatically route messages to a redundant implementation of Service A residing in the public cloud. Similarly, when Database A is unable to process a data access request from
- B. The state management database and resource replication mechanisms can be implemented to establish redundant implementations of Service A and Database A in both on-premise and cloud environments. Using resource replication, a cloud-based duplicate of Service A (Cloud Service A) will be established in a public cloud and will remain in synch with Service A via regular replication cycles. Using the resource replication mechanism together with the state management database mechanism allows for Databa
- C. A cloud bursting solution can be implemented, whereby a redundant copy of Service A is implemented within a public cloud. This cloud-based, redundant implementation of Service A is referred to as Cloud Service A. A copy of Database A is also implemented within the cloud and both the on-premise and cloud-based copies of Database A are redesigned to be nonrelational in order to improve data access performance. Service A continues to act as a first point of contact for Service Consumers A, B and C.
- D. None of the above
Answer : C
Question 9
Cloud Provider X (which owns Cloud X) deploys two physical servers (Physical Servers A and B) and two databases (Databases A and B). Virtual Servers A and B are hosted by
Physical Server A and Ready-Made Environments A and B are hosted by Virtual Server B.
Virtual Servers C and D are hosted by Physical Server B. Cloud Service Consumer A regularly accesses Virtual Server D in order to test and deploy a new cloud service that was developed on-premise by the cloud consumer organization operating Cloud Service
- A. Cloud Service Consumer A is using the IaaS delivery model. Cloud Service Consumer B is using the SaaS delivery model. Customers of the cloud services will be using the PaaS delivery model. The encryption mechanism can be implemented to mitigate the denial of service, insufficient authorization and overlapping trust boundaries security threats.
- B. Cloud Provider X is providing a hybrid delivery model comprised of a combination of the IaaS and PaaS delivery models, which means that Cloud Service Consumers A and B are using both the IaaS and PaaS delivery models. Customers of the cloud services will be using the PaaS delivery model. The single sign-on mechanism can be implemented to mitigate the denial of service and insufficient authorization security threats. The encryption mechanisms can be implemented to mitigate the overlapping trust b
- C. Cloud Service Consumer A is using the IaaS delivery model. Cloud Service Consumer B is using the PaaS delivery model. Customers of the cloud services will be using the SaaS delivery model. An identity and access management mechanism can be implemented to mitigate the denial of service, insufficient authorization and overlapping trust boundaries security challenges.
- D. Cloud Service Consumer A is using the IaaS delivery model. Cloud Service Consumer B is using the PaaS delivery model. Customers of the cloud services will be using the SaaS delivery model. The digital signatures mechanism can be implemented to mitigate the denial of service, insufficient authorization and overlapping trust boundaries security challenges.
Answer : C
Question 10
Cloud Provider Y owns Cloud Y, which provides a set of cloud services, virtual servers and one physical server. Cloud Services A and B are hosted on Virtual Server A, which is
- A. Cloud Provider Y can implement the identity and access management mechanism to mitigate denial of service attacks and can further implement the failover system mechanism (by introducing a redundant physical server with redundant virtual servers) so that when an attack is successful on a given virtual server, a redundant virtual server can take its place.
- B. Cloud Provider Y can move Cloud Service B to Virtual Server A, thereby positioning Virtual Server B as a redundant fallback server used when Virtual Server A is successfully attacked. Similarly, Cloud Provider Yean move Cloud Service A to Virtual Server B, so that Virtual Server A acts as a redundant fallback server for when Virtual Server B is successfully attacked.
- C. Cloud Provider Y can implement a cloud bursting system, whereby Cloud Service A on Virtual Server B automatically takes the place of Cloud Service A on Virtual Server A when that service fails. Similarly, Cloud Service B on Virtual Server A can then automatically take the place of Cloud Service B on Virtual Server A when that service fails.
- D. Cloud Provider Y can introduce a single sign-on mechanism for Virtual Server A to mitigate denial of service threats. The automated scaling listener can then be implemented on Virtual Server B in order to limit the number of instances of Cloud Services A and B. This will prevent Virtual Server B from overloading due to denial of service attacks.
Answer : A
Question 11
The cloud service owner of Cloud Service A is evaluating Clouds X, Y and Z to determine which cloud environment can offer the greatest level of reliability. All three clouds are geographically dispersed across three separate time zones. As a result, each cloud experiences usage peaks at different times. Based on the metrics provided, the greater the usage of a cloud, the lower its reliability. When the cloud service owner complains to Cloud
Provider A (the owner of all three clouds) that none of the clouds provide an adequate level of reliability, Cloud Provider A suggests a solution that increases resiliency.
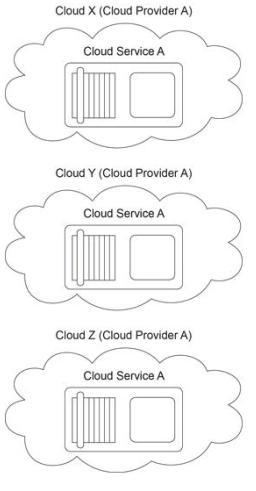
Which of the following statements accurately describe how a cloud balancing solution can be implemented to fulfill the resiliency requirements of Cloud Service A?
- A. Cloud Service A is redundantly deployed in advance within Clouds X. Y and Z and is further supplemented with failover system mechanisms and specialized types of automated scaling listener mechanisms.
- B. Using a PaaS environment, the cloud service owner can configure a primary Cloud Service A implementation on Cloud X so that when failure conditions occur, message requests from cloud service consumers are automatically routed to a redundant on-premise implementation of Cloud Service A. This requires the implementation of the failover system and resource replication mechanisms.
- C. A type of automated scaling listener that can also be considered a cloud monitor is implemented in Clouds X, Y and Z to establish a system whereby each cloud can assume control of cloud service consumer message exchanges. This results in resilient cloud balancing, as opposed to on-demand cloud balancing.
- D. Clouds X, Y and Z are equipped with failover system mechanisms and specialized types of automated scaling listener mechanisms in order to establish cross-cloud resiliency. Cloud Service A is configured so that Clouds X, Y and Z can dynamically generate redundant instances on-demand.
Answer : A,D
Question 12
Cloud Service Consumer A accesses Cloud Service A (1) that resides in Cloud X. a private
- A. Moving Cloud Service A to Cloud Y will require that Database A also be moved to Cloud Y due to the need for Cloud Service A and Database A to share a common virtual server within the same organizational boundary, as required by the cloud-based security group. The move of Database A will increase the integration testing effort and. as a result, will also increase the overall integration costs.
- B. Once Cloud Service A is deployed in Cloud Y, it may form dependencies upon proprietary parts of Cloud Y that may limit its mobility should it be decided to move it outside of Cloud Y in the future. This can incur further locked-in costs that need to be accounted for.
- C. By moving Cloud Service A to Cloud Y, the SaaS delivery model will be established for Cloud Service A, thereby allowing the service implementation to build upon existing infrastructure from underlying PaaS and laaS delivery models that would have been required for Cloud Service B to be implemented in Cloud Y.
- D. Public Cloud Y charges for the use of its IT resources. Moving Cloud Service A to Cloud Y can therefore result in new on-going costs. Although Cloud Service A may be able to share some of the existing IT resources used by Cloud Service B, it will likely incur new on- going costs that need to be budgeted for.
Answer : BD
Question 13
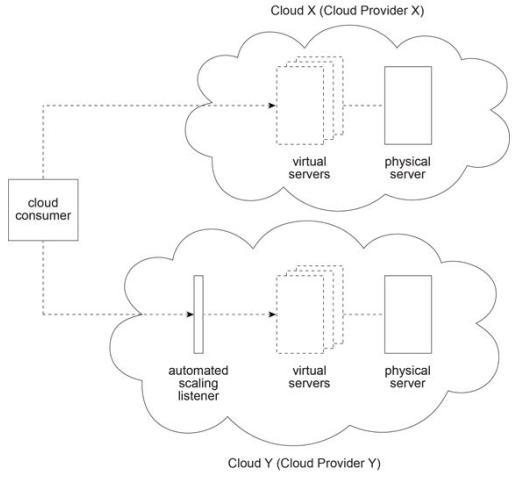
A cloud consumer is interested in leasing cloud-based virtual servers. It compares the virtual servers offered by Cloud Provider X and Cloud Provider Y. Cloud X (owned by
Cloud Provider X) and Cloud Y (owned by Cloud Provider Y) both provide shared physical servers that host multiple virtual servers for other cloud consumers.
The virtual servers on Cloud X are accessed directly, whereas the virtual servers on Cloud
Y are accessed via an automated scaling listener. On Cloud X, virtual servers are pre- configured to support a specific amount of concurrent cloud service consumers. When this threshold is exceeded, cloud service consumer requests are rejected. Due to the use of the automated scaling listener, virtual servers on Cloud Y can provide a greater level of elasticity.
The hourly cost to the cloud consumer to use a virtual server on Cloud X is half that of the cost to use a virtual server on Cloud Y. Within a one month period, Cloud Provider X bases its hourly charge on the maximum number of virtual servers used. Within a one month period, Cloud Provider Y bases its hourly charges on actual virtual server usage. Cloud
Provider Y charges $20 for each hour that a cloud consumer uses a virtual server.
The cloud consumer predicts its monthly usage requirements to be as follows:
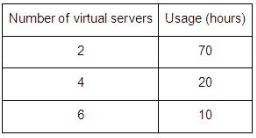
The cloud consumer is required choose the cloud provider with the lowest on-going cost based on its predicted usage. Which of the following statements accurately calculates the on-going usage costs of Cloud Providers X and Y and correctly states the cloud provider that the cloud consumer must choose?
- A. The total usage duration is (10 + 20 + 70) hours = 100 hours. The actual usage is (10 X 6) + (20 X 4) + (70 X 2) hours = 280 hours. The cost of using virtual servers from Cloud Provider X is 100X6X$10 = $6,000. The cost of using virtual servers from Cloud Provider Y is 280 X $20 = $5,600. The cloud consumer must therefore choose Cloud Provider Y.
- B. The total usage duration is (10 + 20 + 70) hours = 100 hours. The actual usage is ((10 X 6) + (20 X 4) + (70 X 2)) x ((2 + 4 + 6) / 3) hours = 1,120 hours The cost of using virtual servers from Cloud Provider Xis10QX6X$10 = $6,000. The cost of using virtual servers from Cloud Provider Y is 1,120 X $20 = $22,400. The cloud consumer must therefore choose Cloud Provider X.
- C. The total usage duration is (10 + 20 + 70) hours = 100 hours. The actual usage is ((10 X 6) + (20 X 4) + (70 X 2)) x ((2 + 4 + 6) / 3) hours = 1,120 hours The cost of using virtual servers from Cloud Provider X is 6 X 100 X $10 = $6,000. The cost of using virtual servers from Cloud Provider Y is 1,120 X $20 = $22,400. The cloud consumer must therefore choose Cloud Provider Y.
- D. The total usage duration is (10 + 20 + 70) x 12 hours = 1.200 hours. The actual usage is (10X6) + (20X4) + (70X2) hours = 280 server hours. The cost of using virtual servers from Cloud Provider Xis12X100X5X$10 = $60,000. The cost of using virtual servers from Cloud Provider Y is 280 X $20 = $5,600. The cloud consumer must therefore choose Cloud Provider Y.
Answer : A
Question 14
Cloud Service Consumer A invokes Cloud Service A from Cloud X (owned by Cloud
Provider X) (1). To fulfill the request from Cloud Service Consumer A, Cloud Service A needs to invoke Cloud Service B that resides on Cloud Y (owned by Cloud Provider Y) (2).
After completing its processing, Cloud Service B sends a response to Cloud Service A (3).
Cloud Service A verifies the response and then finally sends its response to Cloud Service
Consumer A (4).
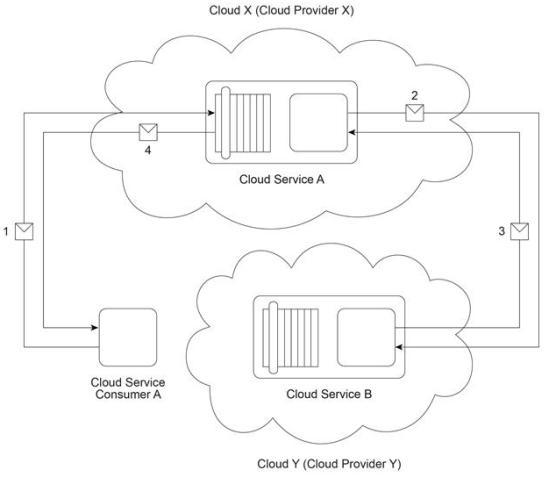
The guaranteed availability of the Cloud Service A implementation is 95% and the guaranteed availability of the Cloud Service B implementation is 95%. Which of the following statements accurately describes the actual availability that Cloud Service
Consumer A can receive based on the described scenario?
- A. Because Cloud Service Consumer A's response message is processed by two separate cloud services, the combined availability increases as follows: 1 - (1 - 0.95) X (1 - 0.95) = 0.9975 or 99.75%
- B. Because Cloud Service A acts as both a cloud service and cloud service consumer in order to process Cloud Service Consumer B's request message, Cloud Service A forms a dependency on Cloud Service B. As a result, the combined availability decreases, as follows: 0.95 X 0.95 = 0.9025 or 90.25%
- C. Cloud Service Consumer A benefits from redundant cloud service implementations, thereby increasing the guaranteed availability as follows: 1 - (1 - (0.95 - 0.1)) X (1 - (0.95 - 0.1)) = 0.9775 or 97.75%
- D. As a result of the dependency formed by Cloud Service Aon Cloud Service B, the combined availability decreases significantly as follows: (0.95 X 0.95) - 0.1 = 0.8025 or 80.25%
Answer : B
Question 15
Cloud Service A is being made available on public Cloud X by Cloud Provider X via the
SaaS delivery model. Cloud Service A is hosted by Physical Server A that also hosts cloud services being used by different cloud service consumers (and owned by different cloud service owners).
Cloud Service Consumers A and B access Cloud Service A on a regular basis and
Physical Server A has been able to accommodate the resulting usage load After reviewing
- A. The multi-device broker mechanism can be implemented to address ubiquitous access requirements by broadening the range of cloud service consumers that can access Cloud Service A. The resilient computing mechanism can be implemented to establish the multitenancy capabilities of Cloud Service A so that it will be able to resiliency accommodate the additional cloud service consumer devices that will gain access to it.
- B. The resilient computing mechanism can be implemented to address ubiquitous access requirements by making Cloud Service A available to a broader range of cloud service consumer devices, including desktops running Web browsers and various mobile devices. The resource replication mechanism can be implemented to enable multi-tenancy within the Cloud Service A implementation.
- C. The resource replication mechanism can be introduced to address ubiquitous access requirements by broadening the range of cloud service consumers that can use Cloud Service A via standard service replication. The virtual server mechanism can be implemented to enable multi-tenancy via each service replication resulting from the application of the resource replication mechanism.
- D. The multi-device broker mechanism can be implemented to address ubiquitous access requirements by broadening the range of cloud service consumers that can access Cloud Service A. The virtual server mechanism can be implemented to establish the multitenancy capabilities of Cloud Service A.
Answer : D