Upgrading Your Skills to MCSA: Windows Server 2016 v1.0
Question 1
Your network contains an Active Directory forest named contoso.com.
You have an Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) farm. The farm contains a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2.
You add a server named Server2 to the farm. Server2 runs Windows Server 2016.
You remove Server1 from the farm.
You need to ensure that you can use role separation to manage the farm.
Which cmdlet should you run?
- A. Update-AdfsRelyingPartyTrust
- B. Invoke-AdfsFarmBehaviorLevelRaise
- C. Set-AdfsFarmInformation
- D. Set-AdfsProperties
Answer : B
Explanation:
AD FS for Windows Server 2016 introduces the ability to have separation between server administrators and AD FS service administrators.
After upgrading our ADFS servers to Windows Server 2016, the last step is to raise the Farm Behavior Level using the Invoke-AdfsFarmBehaviorLevelRaise
PowerShell cmdlet.
To upgrade the farm behavior level from Windows Server 2012 R2 to Windows Server 2016 use the Invoke-ADFSFarmBehaviorLevelRaise cmdlet.
References:
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/mt605334(v=ws.11).aspx
Question 2
HOTSPOT -
You have a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2016. Server1 has the Web Application Proxy role service installed.
You need to publish Microsoft Exchange Server 2013 services through the Web Application Proxy. The solution must use preauthentication whenever possible.
How should you configure the preauthentication method for each service? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
Hot Area:
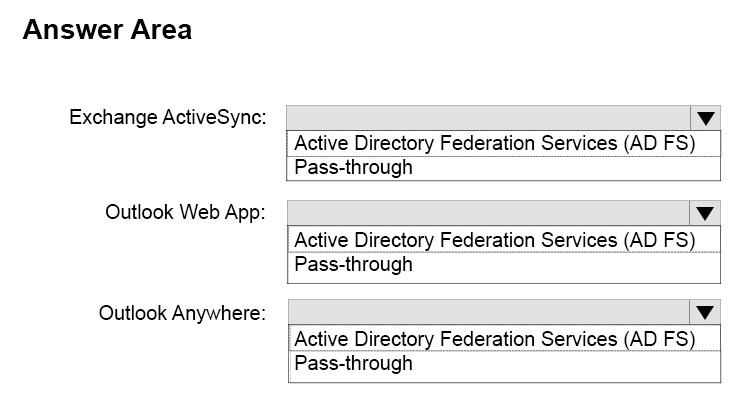
Answer : 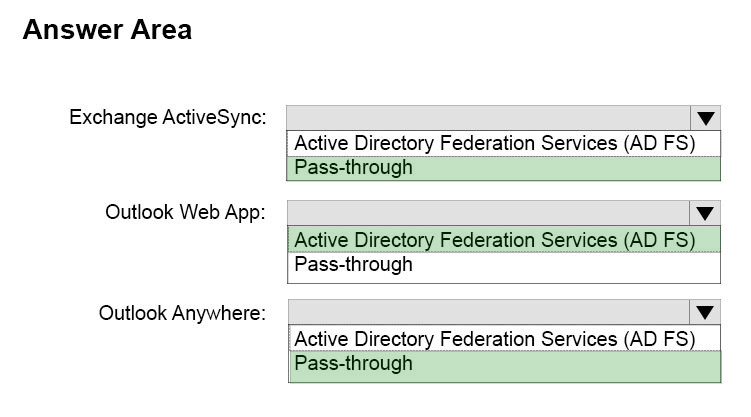
Explanation:
The following table describes the Exchange services that you can publish through Web Application Proxy and the supported preauthentication for these services:
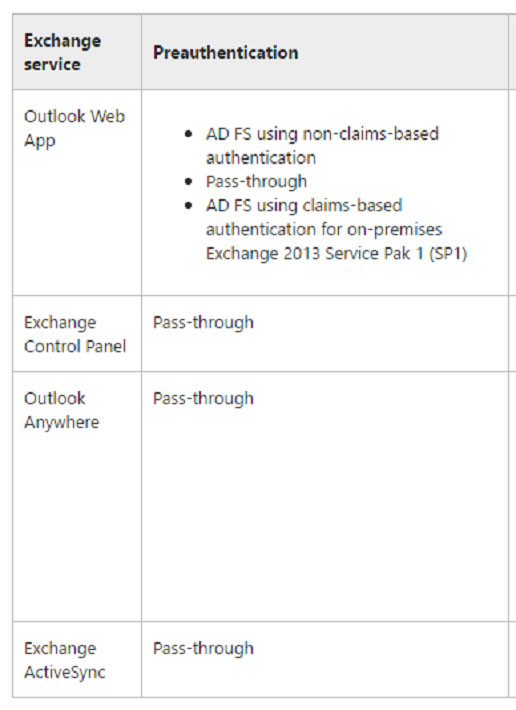
References:
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn528827(v=ws.11).aspx
Question 3
HOTSPOT -
You have a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2016. Server1 has the Web Application Proxy role service installed.
You need to publish Microsoft Exchange ActiveSync services by using the Publish New Application Wizard. The ActiveSync services must use preauthentication.
How should you configure Server1? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
Hot Area:
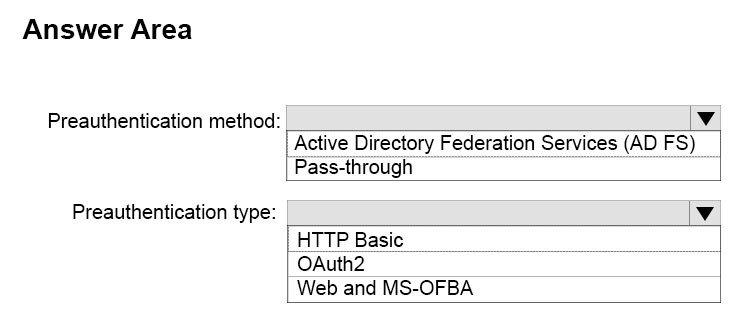
Answer : 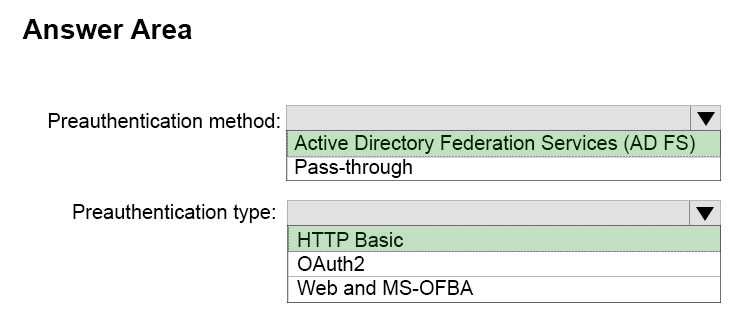
Explanation:
Box 1: Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS)
The well-known HTTP basic authentication that you can use in scenarios such as Exchange Active Sync (ActiveSync). This is a new capability included in this release of Web Application Proxy. For the ActiveSync scenario, the authentication process includes four core steps:
✑ Windows Application Proxy (WAP) stops the request and passes all credentials to AD FS.
✑ AD FS validates, applies policy, and replies with a token.
✑ Upon success, Web Application Proxy allows the request to pass to the Exchange server.
✑ Web Application Proxy caches the token for future use.
Box 2: HTTP Basic -
The well-known HTTP basic authentication that you can use in scenarios such as Exchange Active Sync (ActiveSync).
Question 4
HOTSPOT -
You have a server that runs Windows Server 2016.
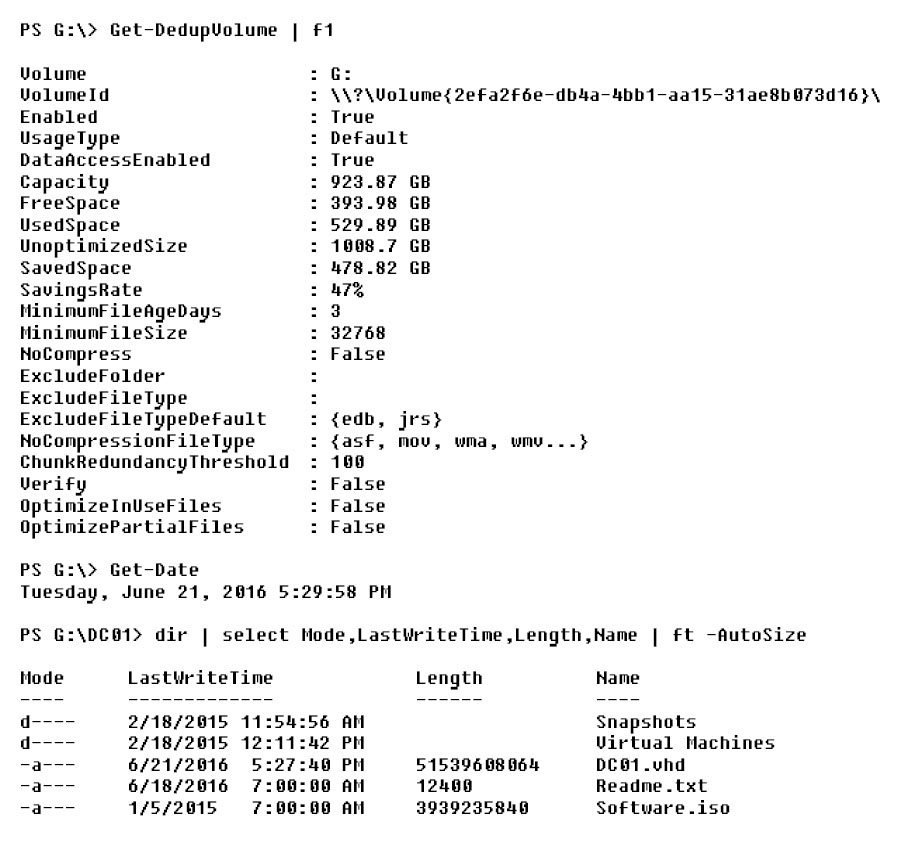
You run the commands shown in the following output.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
Hot Area:

Answer : 
Explanation:
Box 1: No -
The LastWriteTime of DC01.vhd was on June 21, 2016, and the current date is also June 21, 2016, but the MinimumFileAgeDays is 3.
MinimumFileAgeDays specifies a number of days. The deduplication engine optimizes files that users have not accessed in the number of days that you specify. If the last access time is not available, then the deduplication engine uses the last modified time.
Box 2: No -
The size of Readme.txt, 12400 bytes, is less than the Minimum File size, 32768 bytes.
MinimumFileSize specifies the minimum size threshold, in bytes, for files that are optimized. The deduplication engine does not optimize files that do not meet the minimum threshold.
Box 3: Yes -
The Software ISO file is both large and old enough for deduplication.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/module/deduplication/set-dedupvolume?view=win10-ps
Question 5
DRAG DROP -
You have a server that runs Windows Server 2016. You install three additional disks named Disk1, Disk2, and Disk3. You plan to use these physical disks to store data.
You need to create a volume to store data. The solution must prevent data loss in the event of a single disk failure.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:
Answer : 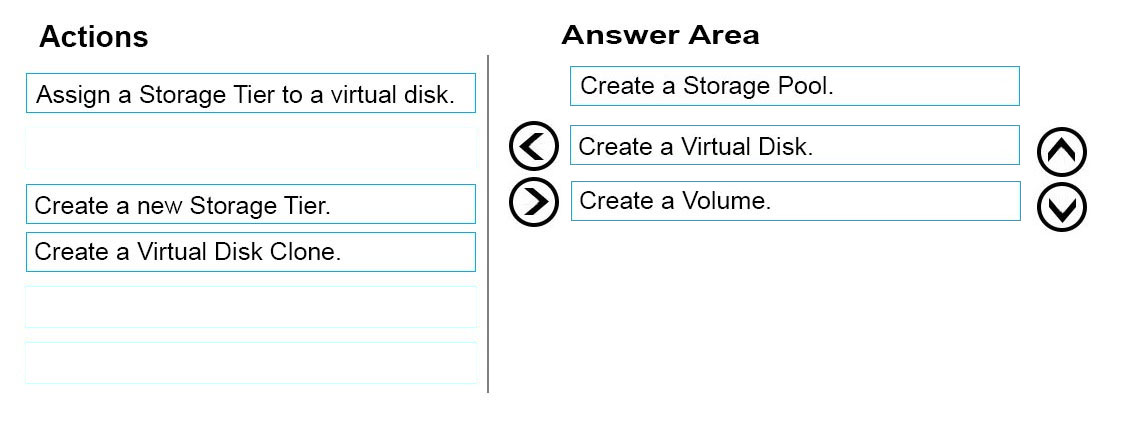
Explanation:
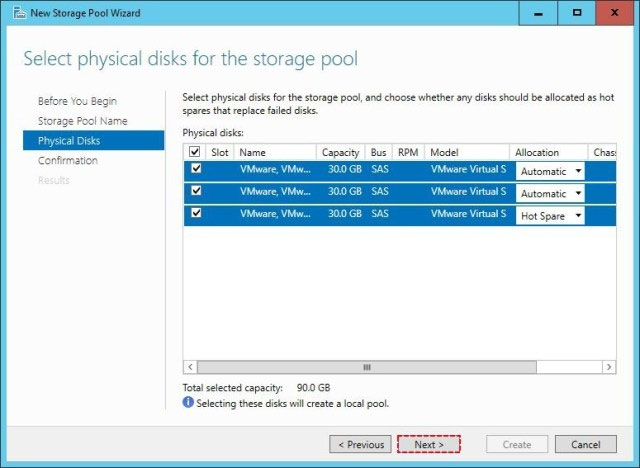
Step 1: Create a Storage Pool -
First we create a Storage Pool. We specify which disks should be included in the storage pool.
Example:
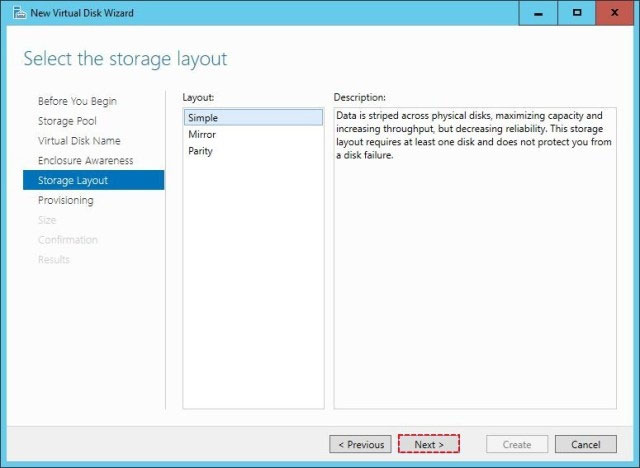
Step 2: Create a Virtual Disk -
After creating the storage pool now start creating a virtual disk for the pool you had created.
✑ When the storage pool wizard finishes, just mark the create a virtual disk option to create a virtual disk after this wizard.
✑ Select the storage pool to create a virtual disk.
Later in the New Virtual Disk wizard you select the Storage Layout. Select Parity.
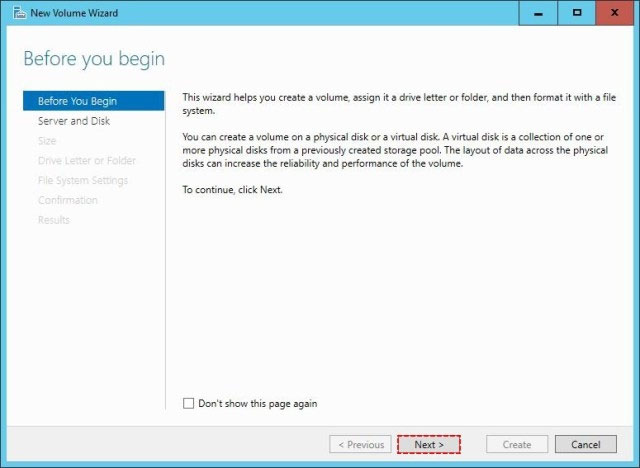
Step 3: Create a Volume -
After creating the virtual disk, create a volume with the New Volume Wizard.
You create the volume on the Virtual Disk you created in Step 2.
References:
http://www.tactig.com/create-a-storage-pool-windows-server/
Question 6
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains two servers named Server1 and Server2 that run Windows Server
2016. The servers have the same hardware configuration.
You need to asynchronously replicate volume F: from Server1 to Server2.
What should you do?
- A. Install the Failover Clustering feature and create a new cluster resource group.
- B. Run Set-DfsrServiceConfiguration and specify the ""RPCPort parameter.
- C. Run New-SRPartnership and specify the ""ReplicationMode parameter.
- D. Install the Failover Clustering feature and use Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV).
Answer : C
Explanation:

-ReplicationMode
Specifies the desired mode of replication for this source and destination pair. The acceptable values for this parameter are:
✑ Synchronous or 1. The synchronous mode requires all writes to commit on the destination server and on the source server, which guarantees data integrity between computers.
✑ Asynchronous or 2. The asynchronous mode writes to the source server without waiting for the destination server, which allows for replication over high latency, geographic networks. The default value is synchronous.
The default asynchronous recovery point alert time is 5 minutes. You can modify it by using the SetSRPartnership cmdlet. The alert time has no effect on replication behavior, only on reporting.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/module/storagereplica/new-srpartnership?view=win10-ps https://msandbu.wordpress.com/2016/05/13/getting-started-with-storage-replica-in-windows-server-2016/ https://www.starwindsoftware.com/blog/how-to-configure-storage-replication-using-windows-server-2016-part-1
Question 7
You have a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2016.
The disks on Server1 are configured as shown in the following table.
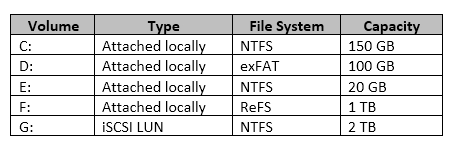
Windows Server 2016 is installed in C:\Windows.
On which two volumes can you enable data deduplication? Each correct answer presents a complete solution.
- A. C:
- B. D:
- C. E:
- D. F:
- E. G:
Answer : CE
Explanation:
Volumes that are candidates for deduplication must conform to the following requirements:
✑ Must not be a system or boot volume. Deduplication is not supported on operating system volumes. (Thus NOT C:)
✑ Can be partitioned as a master boot record (MBR) or a GUID Partition Table (GPT), and must be formatted using the NTFS file system. (Thus NOT D:)
✑ Can reside on shared storage, such as storage that uses a Fibre Channel or an SAS array, or when an iSCSI SAN and Windows Failover Clustering is fully supported.
✑ If you"™re using Windows Server 2012, don"™t deduplicate Cluster Shared Volumes (CSVs). You can access data if a deduplication-enabled volume is converted to a CSV, but you cannot continue to process files for deduplication on Windows Server 2012.
✑ Do not rely on the Microsoft Resilient File System (ReFS). (Thus NOT F:)
✑ Can"™t be larger than 64 TB in size.
✑ Must be exposed to the operating system as non-removable drives. Remotely-mapped drives are not supported.
References:
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh831700(v=ws.11).aspx
Question 8
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same or similar answer choices. An answer choice may be correct for more than one question in the series. Each question is independent of the other questions in this series. Information and details provided in a question apply only to that question.
You have a Hyper-V host named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2016. You plan to deploy several shielded virtual machines on Server1.
You deploy a Host Guardian on a new server.
You need to ensure that Server1 can host shielded virtual machines.
What should you do first?
- A. the Mount-VHD cmdlet
- B. the Diskpart command
- C. the Set-VHD cmdlet
- D. the Set-VM cmdlet
- E. the Set-VMHost cmdlet
- F. the Set-VMProcessor cmdlet
- G. the Install-WindowsFeature cmdlet
- H. the Optimize-VHD cmdlet
Answer : G
Explanation:
Installing Host Guardian Service (HGS) Role
On a machine running Windows Server 2016, install the Host Guardian Service role using Server Manager or Windows PowerShell.
From the command line issue the following command:
Install-WindowsFeature HostGuardianServiceRole ""IncludeManagementTools
References:
https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/datacentersecurity/2016/03/16/windows-server-2016-and-host-guardian-service-for-shielded-vms/
Question 9
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same or similar answer choices. An answer choice may be correct for more than one question in the series. Each question is independent of the other questions in this series. Information and details provided in a question apply only to that question.
You have an Active Directory domain that contains two Hyper-V servers named Server1 and Server2. Server1 has Windows Server 2016 installed. Server2 has
Windows Server 2012 R2 installed.
Each Hyper-V server has three network cards. Each network card is connected to a different subnet. Server1 contains a dedicated migration network.
Server2 contains a virtual machine named VM5.
You plan to perform a live migration of VM5 to Server1.
You need to ensure that Server1 uses all available networks to perform the live migration of VM5.
What should you run?
- A. the Mount-VHD cmdlet
- B. the Diskpart command
- C. the Set-VHD cmdlet
- D. the Set-VM cmdlet
- E. the Set-VMHost cmdlet
- F. the Set-VMProcessor cmdlet
- G. the Install-WindowsFeature cmdlet
- H. the Optimize-VHD cmdlet
Answer : E
Explanation:
Set-VMHost -UseAnyNetworkForMigration
Specifies how networks are selected for incoming live migration traffic. If set to $True, any available network on the host can be used for this traffic. If set to
$False, incoming live migration traffic is transmitted only on the networks specified in the MigrationNetworks property of the host.
PS C:\> Set-VMHost -UseAnyNetworkForMigration $true
This example enables the use of any network for incoming live migrations on the local Hyper-V host.
References:
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh848524.aspx
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/module/hyper-v/set-vmhost?view=win10-ps
Question 10
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same or similar answer choices. An answer choice may be correct for more than one question in the series. Each question is independent of the other questions in this series. Information and details provided in a question apply only to that question.
You have a Hyper-V host named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2016. Server1 has a virtual machine that uses a virtual hard disK (VHD) named disk1.vhdx.
You receive the following warning message from Event Viewer: "One or more virtual hard disks have a physical sector size that is smaller than the physical sector size of the storage on which the virtual hard disk file is located."
You need to resolve the problem that causes the warning message.
What should you run?
- A. the Mount-VHD cmdlet
- B. the Diskpart command
- C. the Set-VHD cmdlet
- D. the Set-VM cmdlet
- E. the Set-VMHost cmdlet
- F. the Set-VMProcessor cmdlet
- G. the Install-WindowsFeature cmdlet
- H. the Optimize-VHD cmdlet
Answer : C
Explanation:
Issue -
One or more virtual hard disks have a physical sector size that is smaller than the physical sector size of the storage on which the virtual hard disk file is located.
Resolution -
Do one of the following:
* Perform a storage migration to move the virtual hard disk to a new physical system
* Use a registry setting to enable a VHD-format virtual hard disk to report a physical sector size of 4k
* Use Windows PowerShell or WMI to enable a VHDX-format virtual hard disk to report a specific sector size
The Set-VHD cmdlet sets the ParentPath or PhysicalSectorSizeBytes properties of a virtual hard disk. The two properties must be set in separate operations.
The Set-VHD -PhysicalSectorSizeBytes parameter specifies the physical sector size, in bytes. Valid values are 512 and 4096. This parameter is supported only on a VHDX-format disk that is not attached when the operation is initiated.
References:
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server-docs/compute/hyper-v/best-practices-analyzer/avoid-using-virtual-hard-disks-with-sector-size-less-than-size- of-physical https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh848561.aspx
Question 11
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same or similar answer choices. An answer choice may be correct for more than one question in the series. Each question is independent of the other questions in this series. Information and details provided in a question apply only to that question.
You have a Hyper-V host named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2016. Server1 contains a virtual machine named VM1.
You need to ensure that you can use nested virtualization on VM1.
What should you run on Server1?
- A. the Mount-VHD cmdlet
- B. the Diskpart command
- C. the Set-VHD cmdlet
- D. the Set-VM cmdlet
- E. the Set-VMHost cmdlet
- F. the Set-VMProcessor cmdlet
- G. the Install-WindowsFeature cmdlet
- H. the Optimize-VHD cmdlet
Answer : F
Explanation:
Configure Nested Virtualization -
✑ Create a virtual machine.
✑ While the virtual machine is in the OFF state, run the following command on the physical Hyper-V host. This enables nested virtualization for the virtual machine.
Set-VMProcessor -VMName <VMName> -ExposeVirtualizationExtensions $true
References:
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/virtualization/hyperv_on_windows/user_guide/nesting
Question 12
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same or similar answer choices. An answer choice may be correct for more than one question in the series. Each question is independent of the other questions in this series. Information and details provided in a question apply only to that question.
You have a Hyper-V host named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2016. Server1 has a dynamically expanding virtual hard disk (VHD) file that is 900 GB. The
VHD contains 400 GB of free space.
You need to reduce the amount of disk space used by the VHD.
What should you run?
- A. the Mount-VHD cmdlet
- B. the Diskpart command
- C. the Set-VHD cmdlet
- D. the Set-VM cmdlet
- E. the Set-VMHost cmdlet
- F. the Set-VMProcessor cmdlet
- G. the Install-WindowsFeature cmdlet
- H. the Optimize-VHD cmdlet
Answer : H
Explanation:
The Optimize-VHD cmdlet optimizes the allocation of space in or more virtual hard disk files, except for fixed virtual hard disks. The Compact operation is used to optimize the files. This operation reclaims unused blocks as well as rearranges the blocks to be more efficiently packed, which reduces the size of a virtual hard disk file.
References:
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/itpro/powershell/windows/hyper-v/optimize-vhd
Question 13
You have a Hyper-V host named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2016. Server1 hosts a virtual machine named VM1.
You need to provide VM1 with direct access to a graphics processing unit (GPU) on Server1.
What should you do first?
- A. On VM1, install the Quality Windows Audio Video Experience (qWave) feature.
- B. Disable the display adapter device on Server1.
- C. In the settings of VM1, add a RemoteFX 3D Video Adapter.
- D. Dismount the display adapter on Server1.
Answer : B
Explanation:
Before the physical device is allowed to be passed through to the VM, the device must be disabled on the host system. The physical device must be accessible/ available exclusively to the VM only.
References: Introduction to Windows Server 2016 Hyper-V Discrete Device Assignment, page 5 https://lenovopress.com/lp0088.pdf
Question 14
HOTSPOT -
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains three servers named Server1, Server2, and Server3 that run
Windows Server 2016.
Server1 has IP Address Management (IPAM) installed. Server2 and Server3 have the DHCP Server role installed and have several DHCP scopes configured. The
IPAM server retrieves data from Server2 and Server3.
A domain user named User1 is a member of the groups shown in the following table.
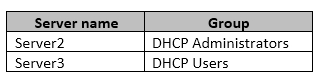
On Server1, you create a security policy for User1. The policy grants the IPAM DHCP Scope Administrator Role with the \Global access scope to the user.
Which actions can User1 perform? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
Hot Area:
Answer : 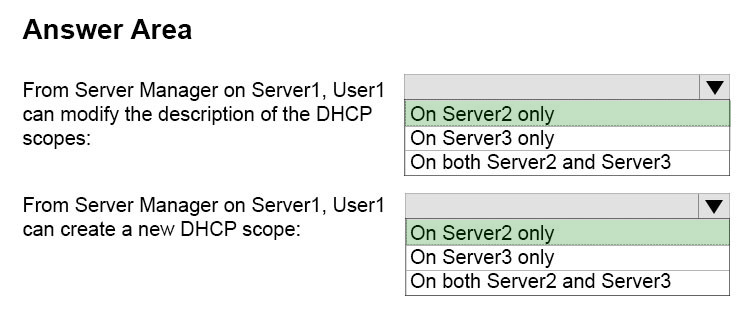
Explanation:
User1 is using Server Manager, not IPAM to perform the administration. Therefore, only the "DHCP Administrators" permission on Server2 and the "DHCP Users" permissions on Server3 are applied.
The permissions granted through membership of the "IPAM DHCP Scope Administrator Role" are not applied when the user is not using the IPAM console.
Question 15
You have two Hyper-V hosts named Server1 and Server2 that run Windows Server 2016.
The following virtual switches are configured on the Hyper-V hosts.
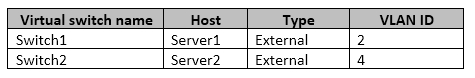
The following virtual machines run on the Hyper-V hosts.
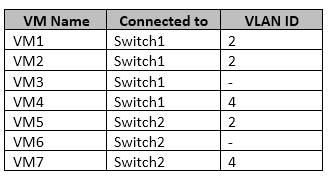
All virtual machines have IP addresses from the 192.168.1.0/24 network. VLANs are configured in Hyper-V only. Physical switches are not configured with VLANs.
To which virtual machine or virtual machines can VM1 connect?
- A. VM2, VM3, VM5 and VM6 only
- B. VM2, VM3 and VM4 only
- C. VM2 only
- D. VM2 and VM5 only
Answer : D
Explanation:
If the port is set to a specific VLAN, then that port becomes a member of that VLAN. Its frames are still untagged, but the switch will only allow that port to communicate with other devices on the same VLAN.
References:
http://www.altaro.com/hyper-v/setting-up-vlans-in-hyper-v/