Configuring Windows 8.1 v12.0
Question 1
A company has an Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) domain. All client computers run Windows 7.
You plan to upgrade the client computers to Windows 8.1 Pro.
You need to choose the methods that do not require the manual entry of a product key during the upgrade.
Which two methods should you choose? (Each correct answer presents a complete solution. Choose two.)
- A. Use the Windows 8.1 online upgrade tool.
- B. Use Group Policy to assign the Windows 8.1 installation file to the client computers.
- C. Use the Microsoft Deployment Toolkit.
- D. Extract the contents of the Windows 8.1 .iso image file to a new shared folder and run the setup program from that folder.
Answer : CD
Explanation:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn475741.aspx
Microsoft Deployment Toolkit -
The Microsoft Deployment Toolkit (MDT) provides a unified collection of tools, processes, and guidance for automating desktop and server deployments. In addition to reducing deployment time and standardizing desktop and server images, MDT offers improved security and ongoing configuration management. http://www.technize.net/install-windows-8-install-pxe-boot-network-lan/
How To Install Windows 8 Over The Network (LAN)
6. Now share the folder in which Windows 8 setup files are located. At least one user should be able to read the network folder to be able to run the setup remotely. http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh824952.aspx
Windows Setup Edition Configuration and Product ID Files (EI.cfg and PID.txt)
Applies To: Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2
The edition configuration (EI.cfg) file and the product ID (PID.txt) file are optional configuration files that you can use to specify the Windows product key and the Windows edition during Windows installation. You can use these files to automate the product-key entry page in Windows Setup instead of using an answer file. If you use an EI.cfg file to differentiate volume license media, but you do not include a PID.txt file, the user receives a prompt for a product key to continue Windows Setup.
You can reuse the product key in the product ID file for multiple installations. The product key in the product ID file is only used to install Windows. This key is not used to activate
Windows.
Question 2
A computer currently runs a 64-bit version of Windows 7 Enterprise.
You need to deploy a 64-bit version of Windows 8.1 Pro to the computer. The new deployment must not affect the Windows 7 installation on the computer.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence? (To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.)
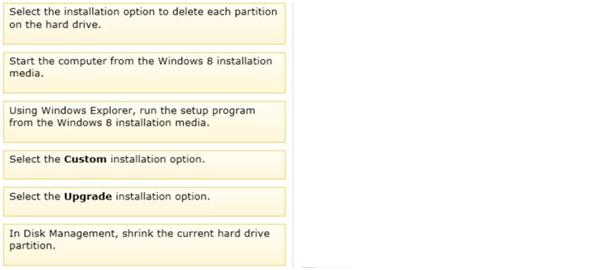
Answer : 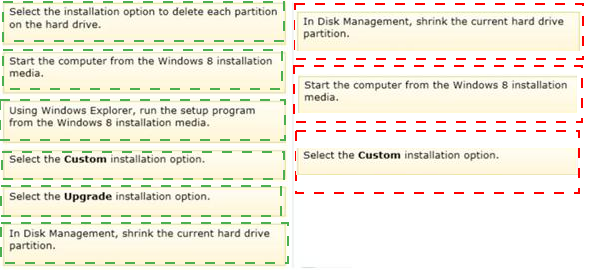
Explanation:
Windows 8 Tip: Dual-Boot with Windows 7
When it comes to dual-booting between Windows 8 and Windows 7, the advice is the same as always: Install the older OS first, make room for the second OS, and then install the newer OS.
Once Windows 7 is installed on the PC, there are two steps to follow to install Windows 8 in a dual-boot configuration:
1. Partition the disk.
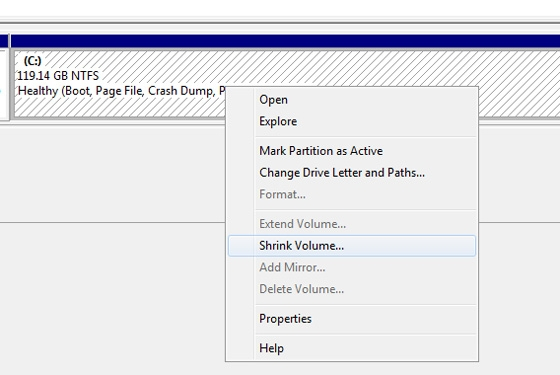
2. Install Windows 8 using the Custom install type. Now, you can run Windows 8 Setup.
You can use optical disc- or USB-based Setup media, but you must do so by booting the
PC from the media. (That is, do not run Setup from within Windows 7.)
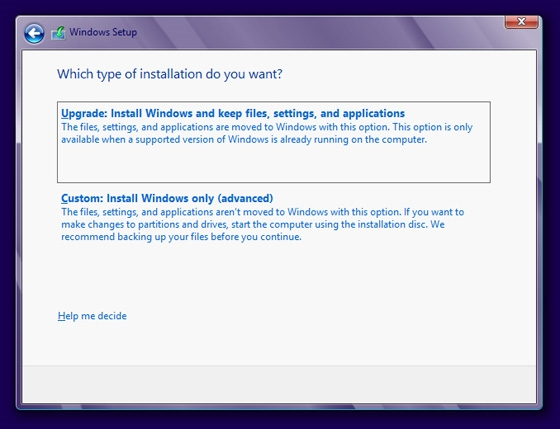
Step through the Windows 8 Setup wizard normally. When you reach the screen that asks,
Which type of installation do you want?, Choose Custom: Install Windows only
(advanced).
Question 3
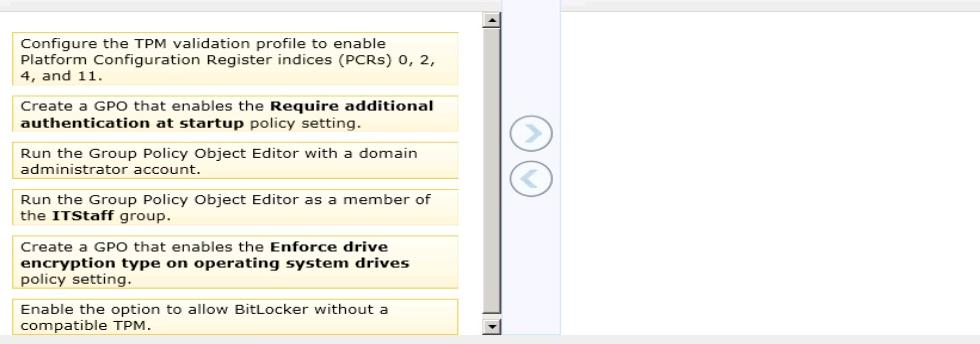
A company has an Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) domain. All client computers run Windows 8.1. Some computers have a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) chip. Members of the ITStaff security group are part of the local Power Users group on each client computer.
You need to configure a single Group Policy object (GPO) that will allow Windows
BitLocker Drive Encryption on all client computers by using the least amount of privilege necessary.
Which commands should you run? (To answer, drag the appropriate command or commands to the correct location or locations in the answer area. Commands may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.)
Answer : 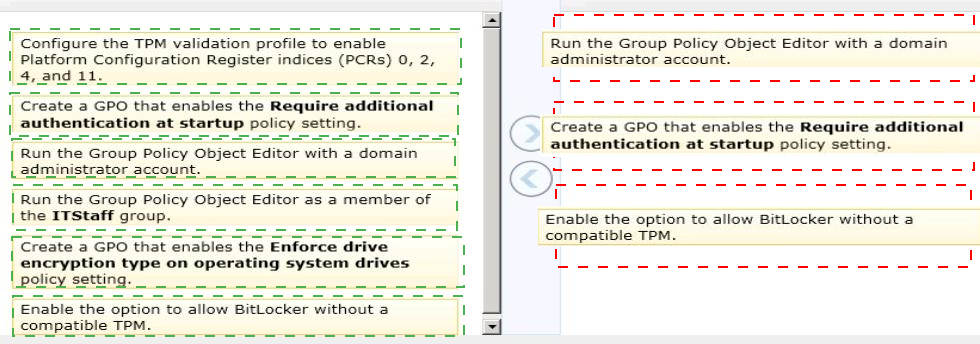
Explanation:
Ref: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ee706521(v=ws.10).aspx http://technet.microsoft.com/en-US/library/cc754948.aspx
Group Policy Planning and Deployment Guide
Administrative requirements for Group Policy
To use Group Policy, your organization must be using Active Directory, and the destination desktop and server computers must be running Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista,
Windows Server 2003, or Windows XP.
By default, only members of the Domain Admins or the Enterprise Admins groups can create and link GPOs, but you can delegate this task to other users. http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj679890.aspx
BitLocker Group Policy Settings -
Require additional authentication at startup
This policy setting is used to control which unlock options are available for operating system drives.
With this policy setting, you can configure whether BitLocker requires additional authentication each time the computer starts and whether you are using BitLocker with a
Trusted Platform Module (TPM). This policy setting is applied when you turn on BitLocker.
Reference -
If you want to use BitLocker on a computer without a TPM, select the Allow BitLocker without a compatible TPM check box. In this mode, a USB drive is required for startup. Key information that is used to encrypt the drive is stored on the USB drive, which creates a
USB key. When the USB key is inserted, access to the drive is authenticated and the drive is accessible. If the USB key is lost or unavailable, you need to use one of the BitLocker recovery options to access the drive.
Further information:
Enforce drive encryption type on fixed data drives
This policy controls whether fixed data drives utilize Used Space Only encryption or Full encryption. Setting this policy also causes the BitLocker Setup Wizard to skip the encryption options page so no encryption selection displays to the user.
Question 4
You administer Windows 8.1 client computers in your company network.
You receive a virtual hard disk (VHD) file that has Windows 8.1 Pro preinstalled, along with several business applications.
You need to configure your client computer to start from either the VHD file or from your current operating system.
Which three actions should you perform? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose three.)
- A. Import the contents of the system store from a file.
- B. Export the contents of the system store into a file.
- C. Attach the VHD file by using Disk Management.
- D. Make the VHD disk bootable.
- E. Create a new empty boot configuration data store.
- F. Create a new entry in the boot configuration data store.
Answer : C,D,F
Explanation: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/gg318049%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
Creating Bootable Virtual Hard Disks
Using the Disk Management Tools -
This section describes how to create a bootable VHD by using the Disk Management tools.
You create a VHD and then apply a Windows image from a .wim file to a partition in the
VHD. After you complete the steps in this section, you can configure the VHD for native boot or configure it to boot in a virtual machine by following the instructions in Preparing
Virtual Hard Disks for Boot.
http://blogs.technet.com/b/haroldwong/archive/2012/08/18/how-to-create-windows-8-vhd- for-boot-to-vhd-using-simple-easy-to-follow-steps.aspx
How to Create Windows 8 VHD for Boot to VHD using simple, easy to follow steps
I. Once I make a backup copy of the VHD file for future use, I will go ahead and Mount the
VHD again to add that installation to the boot menu. To do this, I will right click Disk
Management and select Attach VHD. The Attach VHD Wizard will start. I can either browse to the VHD or just type it in the Location field.
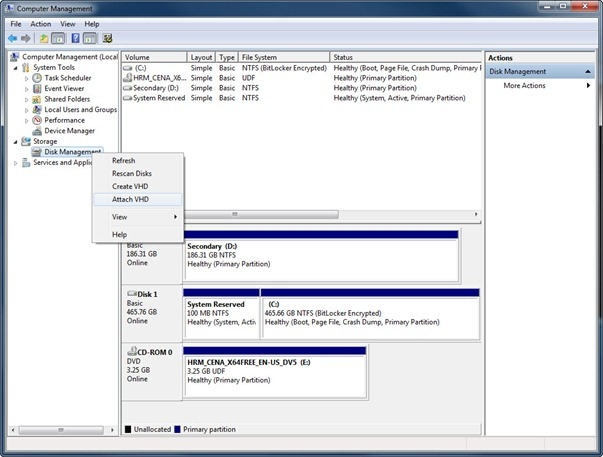
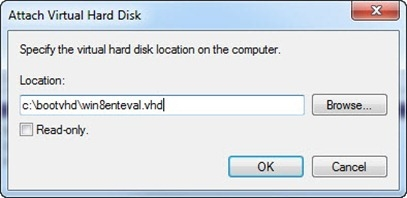
J. The VHD will be mounted and will be assigned a drive letter by the system. In my case, it is drive F: again.
K. Go back to the Administrative Command Prompt and type the following command to add the installation to the Boot Menu: bcdboot F:\windows
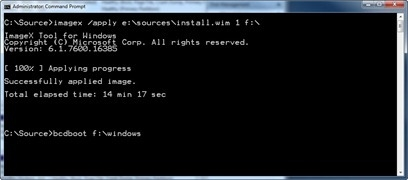
L. Once the command finishes, you will now have the new Windows 8 entry in your boot menu.
Further Information:
F: Commands to add an existing VHD to your boot menu:
bcdedit /copy {originalguid} /d "New Windows 7 Installation" bcdedit /set {newguid} device vhd=[D:]\Image.vhd bcdedit /set {newguid} osdevice vhd=[D:]\Image.vhd bcdedit /set {newguid} detecthal on
Question 5
A company has client computers that run Windows 8.1. All client computers allow incoming
Remote Desktop connections.
You attempt to connect from COMPUTER1 to COMPUTER2 by using Remote Desktop.
Remote Desktop cannot connect to the remote computer. You establish that the firewall settings on COMPUTER2 have not been set to allow incoming connections.
From COMPUTER1, you need to enable Remote Desktop traffic through Windows Firewall on COMPUTER2.
Which commands should you run? (To answer, drag the appropriate command or commands to the correct location or locations in the answer area. Commands may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.)
Answer : 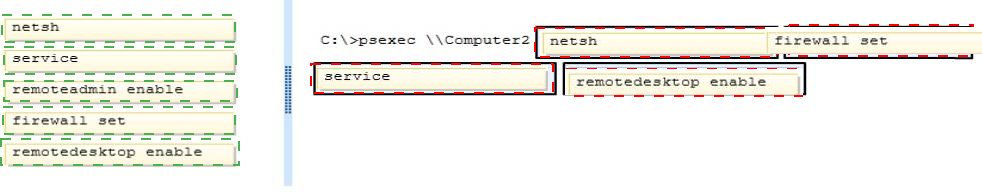
Explanation:
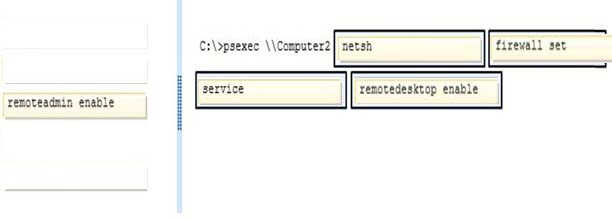
Ref: http://docs.oseems.com/operatingsystem/windows/firewall-command http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/bb897553.aspx
PsExec -
PsExec is a light-weight telnet-replacement that lets you execute processes on other systems, complete with full interactivity for console applications, without having to manually install client software. PsExec's most powerful uses include launching interactive command-prompts on remote systems and remote-enabling tools like IpConfig that otherwise do not have the ability to show information about remote systems. http://ss64.com/nt/psexec.html
PsExec -
Syntax -
psexec \\computer[,computer[,..] [options] command [arguments] http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc771046%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
Netsh Commands for Windows Firewall
The Netsh commands for Windows Firewall provide a command-line alternative to the capabilities of the Windows Firewall Control Panel utility. By using the Netsh firewall commands, you can configure and view Windows Firewall exceptions and configuration settings.
Netsh firewall -
The following sections describe each command and its syntax.
set service
Enables or disables the pre-defined file and printer sharing, remote administration, remote desktop, and UPnP exceptions.
Syntax -
set service [ type = ] { fileandprint | remoteadmin | remotedesktop | upnp | all } [ [ mode = ] { enable | disable } ] [ [ scope = ] { all | subnet | custom } ] [ [ addresses = ] { IPAddress |
IPRange | Subnet | localsubnet }[,] ] [ [ profile = ] { current | domain | standard | all } ]
Parameters -
[ type = ] { fileandprint | remoteadmin | remotedesktop | upnp | all }
Required. Specifies the service whose pre-defined rules are enabled or disabled. The value must be one of the following: fileandprint. The file and printer sharing service. remoteadmin. The ability to remotely administer a computer running Windows. remotedesktop. The ability to use a Terminal Services client such as Remote Desktop. upnp. Universal Plug-and-Play protocol for networked devices. all. All of the above services.
[ [ mode = ] { enable | disable } ]
Specifies whether this exception is currently applied and active on the local computer. The default value is enable.
[ [ scope = ] { all | subnet | custom } ]
[ [ addresses = ] { IPAddress | IPRange | Subnet | localsubnet }[,] ]
[ [ profile = ] { current | domain | standard | all } ]
Question 6
A company has an Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) domain. All client computers run Windows 8.1. Portable client computers connect to the corporate wireless network.
You have the following requirements:
-> Prevent users from configuring a wireless network by using settings from a USB flash drive.
-> Do not affect the use of other USB devices.
You need to create a Group Policy object (GPO) to meet the requirements.
Which GPO should you create?
- A. A GPO that disables the Allow only USB root hub connected Enhanced Storage Features policy setting.
- B. A GPO that enables wireless policy processing.
- C. A GPO that prohibits connections to mobile broadband networks when roaming.
- D. A GPO that configures Windows Connect Now settings.
Answer : D
Explanation:
http://windows.microsoft.com/en-US/windows-vista/What-is-Windows-Connect-Now
Computer Configuration\Policies\Administrative Templates\Network\Windows Connect Now
Turn Off Ability To Configure Using A USB Flash Drive setting:
Prevents Windows from being able to store a Windows Connect Now configuration to a
UFD. Because the Windows Connect Now information stored on a UFD contains information that can allow computers to access your protected wireless network, you might choose to disable this setting to improve the security of your wireless networks. http://sourcedaddy.com/windows-7/windows-connect-now-in-windows-7.html http://windows.microsoft.com/en-US/windows-vista/What-is-Windows-Connect-Now
What is Windows Connect Now?
Microsoft Windows Connect Now (WCN) is a technology designed to address the need for a simple and more secure way to configure network devices and computers. In addition to easier device configuration, you can use WCN to save wireless network settings to a USB flash drive and then plug that drive into devices (such as routers) and computers so you can quickly and easily add them to a network. http://support.epson.ru/products/manuals/101846/html_z/setpn_4.htm
Using WCN (Windows Connect Now)
Question 7
A company has an Active Directory Domain Services domain. All client computers run
Windows 8.1 and are joined to the domain.
You run the ipconfiq command on a client computer. The following output depicts the results.
Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection 3:
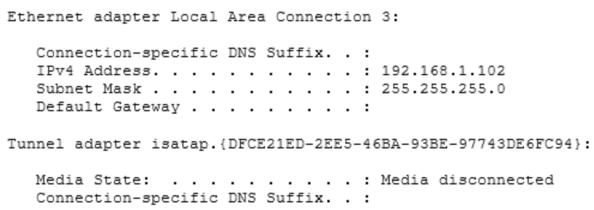
You need to ensure that you can establish a DirectAccess connection from the client computer to the network.
What should you do?
- A. Create a new VPN connection.
- B. Remove the computer from the domain.
- C. Enable IPv6 on the network adapter.
- D. Configure a static IPv4 address.
Answer : C
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd637767%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
DirectAccess Connections -
DirectAccess overcomes the limitations of VPNs by automatically establishing a bi- directional connection from client computers to the corporate network. DirectAccess is built on a foundation of proven, standards-based technologies: Internet Protocol security (IPsec) and Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6).
Further Information:
http://john.bryntze.net/jbkb-v2/certification-exam-70-687-configuring-windows-8-part-3- configure-network-connectivity-15/
A few Windows 8 functions only work with IPv6 such as DirectAccess and HomeGroup.
Question 8
A company has client computers that run Windows 8.1. File History is on.
An employee downloads data to a folder on drive D named Archives.
You need to ensure that the user can restore files from the Archives folder by using File
History.
What should you do?
- A. Configure the File History advanced settings to include the Archives folder.
- B. From the File History configuration options, change the drive and select the Archives folder.
- C. Create a library named History and add the Archives folder to the library.
- D. Move the Archives folder into the Windows system folder.
Answer : C
Explanation:
http://blogs.msdn.com/b/b8/archive/2012/07/10/protecting-user-files-with-file-history.aspx
What is File History?
File History is a backup application that continuously protects your personal files stored in
Libraries, Desktop, Favorites, and Contacts folders. It periodically (by default every hour) scans the file system for changes and copies changed files to another location. Every time any of your personal files has changed, its copy will be stored on a dedicated, external storage device selected by you. Over time, File History builds a complete history of changes made to any personal file. http://blogs.windows.com/windows/b/extremewindows/archive/2012/12/20/a-new-way-to- backup-file-history-in-windows-8.aspx
A New Way to Backup: File History in Windows 8
File History is a new feature in Windows 8 that helps to ensure that your personal files are safe. In addition to being a backup solution, File History also provides the capability to restore multiple backup copies (versions) of your files. File history in Windows 8 is easy to setup, powerful, and reliable. This means you can have more confidence when working with files, and also keep less redundant copies around for your own personal data history.
You can easily configure File History to protect some or all of the files that are in your libraries on Windows 8. You can add folders to your libraries easily in Windows 8, giving you the ability to use File History with any group of folders and files that you choose.
Question 9
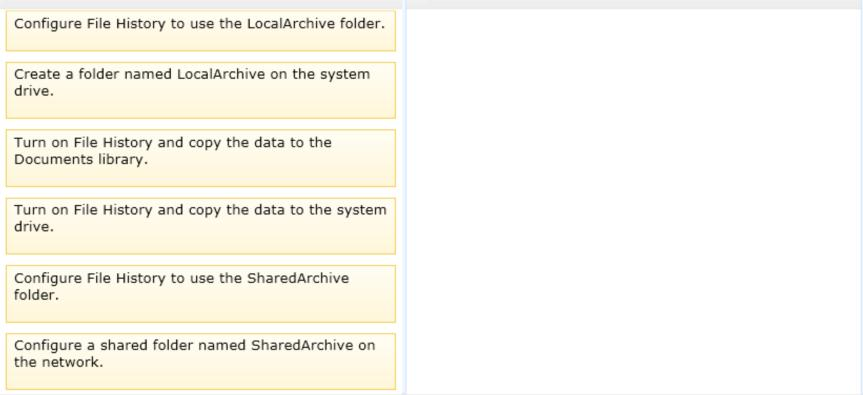
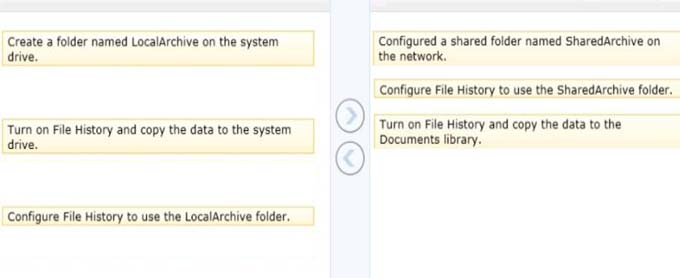
A company has a branch office with client computers that run Windows 8.1. Files are saved locally on the client computers and are not backed up regularly.
You need to ensure that you can retrieve previous versions of locally saved files from each client computer.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence? (To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.)
Answer : 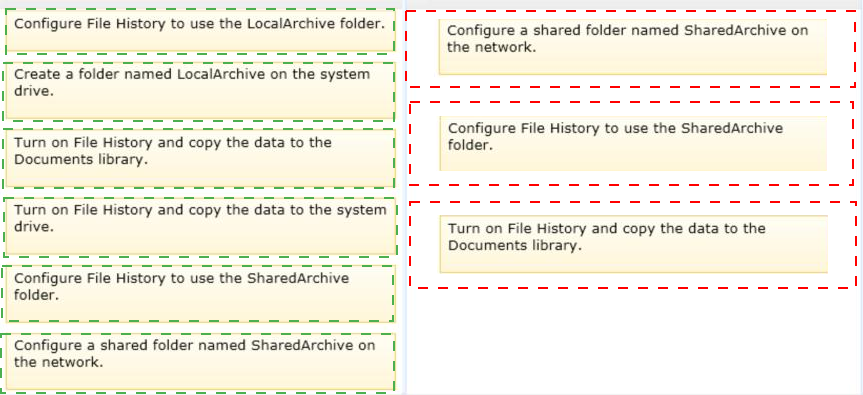
Explanation:
Ref: http://blogs.msdn.com/b/b8/archive/2012/07/10/protecting-user-files-with-file- history.aspx http://blogs.msdn.com/b/b8/archive/2012/07/10/protecting-user-files-with-file-history.aspx
What is File History?
File History is a backup application that continuously protects your personal files stored in
Libraries, Desktop, Favorites, and Contacts folders. It periodically (by default every hour) scans the file system for changes and copies changed files to another location. Every time any of your personal files has changed, its copy will be stored on a dedicated, external storage device selected by you. Over time, File History builds a complete history of changes made to any personal file.
Requirements -
File History requires:
Windows 8 Client operating system
An external storage device with enough storage capacity to store a copy of all user libraries, such as a USB drive, Network Attached Storage device, or share on another PC in the home network.
Question 10
A company has an Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) domain. All client computers run Windows 8.1. Client computers use Window BitLocker Drive Encryption with a Trusted
Platform Module (TPM) chip.
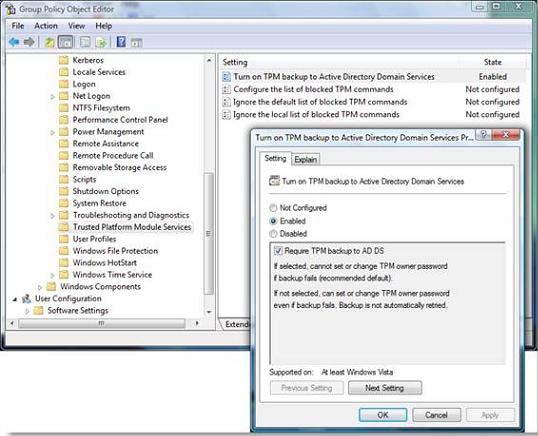
You need to create a Group Policy object (GPO) that will secure the TPM owner information.
Which policy setting should you configure?
- A. Enable the Turn on TPM backup to Active Directory Domain Services policy setting.
- B. Enable the Configure the level of TPM usage authorization information available to the registry policy setting.
- C. Set the Configure the level of TPM owner authorization information available to operating system policy setting to Full.
- D. Enable the Configure TPM platform validation profile policy setting.
Answer : A
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj679889.aspx
Trusted Platform Module Services Group Policy Settings
If you enable this policy setting, TPM owner information will be automatically and silently backed up to AD DS when you use Windows to set or change a TPM owner password.
Question 11
An organization has client computers that run Windows 7.
You install the Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit (ADK) in the environment.
You capture user settings and data files to a network share, and then perform a clean installation of Windows 8.1 on the client computers.
You need to apply the user profiles from the Windows 7 installation to the Windows 8.1 installation.
What should you do?
- A. Run the Ioadstate command.
- B. Copy the Default Profile to a folder on drive C.
- C. Run the scanstate command.
- D. Run Windows Easy Transfer and select the user profile to migrate.
- E. Run the ImageX command
Answer : A
Explanation: http://4sysops.com/archives/windows-8-migration-user-data-and-settings/
Windows 8 migration User data and settings
User State Migration Tools (USMT)
You can extract the USMT tools from the Windows ADK.
USMT is revised to version 5.0 for Windows Server 2012 and Windows 8, and consists of the following three programs:
Scanstate.exe: This tool performs the user state backup
Loadstate.exe: This tool performs the user state restore
Usmtutils.exe: This tool enables you to verify compressed migration store files as well as extract contents from them
Question 12
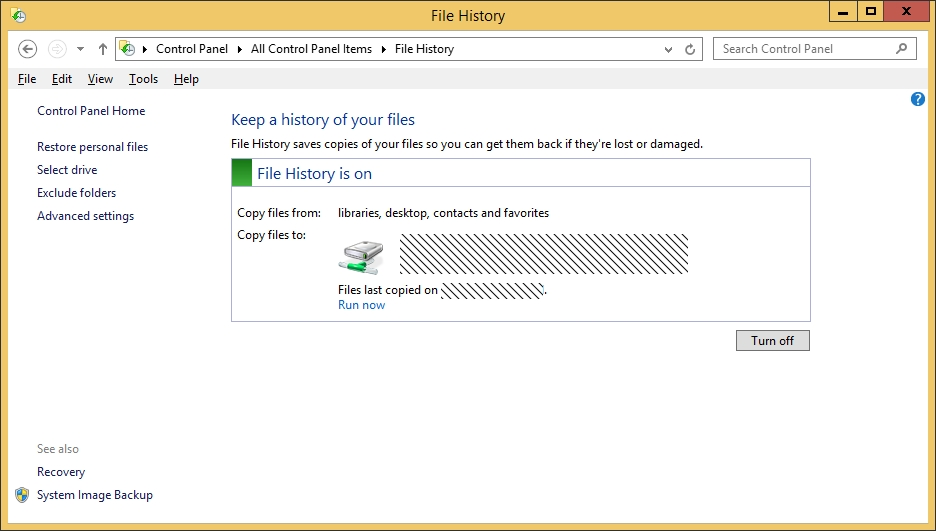
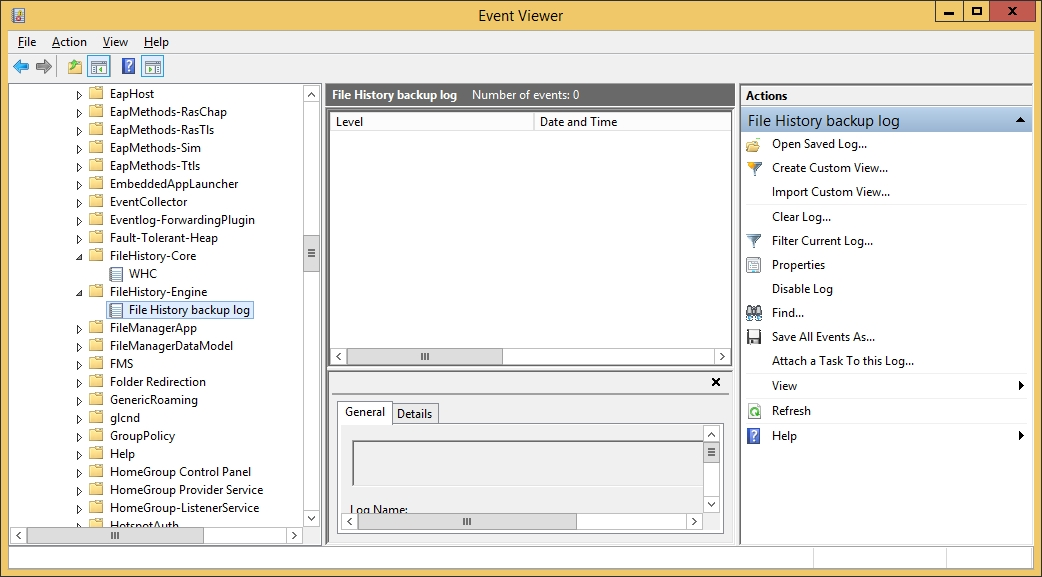
A company has client computers that run Windows 8.1. Finance department employees store files in the C:\Finance directory. File History is on.
A Finance department employee attempts to restore a file to a previous version by using
File History. The file is not available to restore.
You need to establish why the file history is not available and ensure that it is available in the future.
Which two actions should you perform? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution.
Choose two.)
- A. Review the File History backup log.
- B. Move the file into a library.
- C. Restore the data files from the Previous Versions tab located in the folder properties.
- D. Set the Protection Settings for drive C to On.
Answer : AB
Explanation:
http://blogs.windows.com/windows/b/extremewindows/archive/2012/12/20/a-new-way-to- backup-file-history-in-windows-8.aspx
File History only backs up data in libraries, favorites, desktop, and contacts and must use a non-system drive for backup.
Since File History is already on we can assume the drive doesn't need to be changed. So we should review the log and move the file to a library.
Question 13
A company has client computers that run Windows 8.1. The client computer systems frequently use IPSec tunnels to securely transmit data.
You need to configure the IPSec tunnels to use 256-bit encryption keys.
Which encryption type should you use?
- A. 3DES
- B. DES
- C. RSA
- D. AES
Answer : D
Explanation: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd125356%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
Descriptions of the IPsec Algorithms and Methods
Encryption algorithms -
Data encryption algorithms are used to provide confidentiality to the data payload of an
IPsec-protected network packet. Encryption algorithms can be very computationally intensive and can significantly impact computer performance. We recommend that you only encrypt network traffic that requires encryption. If you find that encryption impacts performance more than expected, consider using a network adapter that supports IPsec task offload.
DES -
DES is a block cipher encryption protocol that uses a 56-bit key and is documented in
Federal Information Processing Standards Publication 46-3
(http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=128014). A block cipher is an encryption algorithm that operates on a fixed size block of data. DES encrypts data in 64-bit blocks using a 64- bit key. The key appears to be a 64-bit key, but one bit in each of the 8 bytes is used for error checking, resulting in 56 bits of usable key.
3DES
Triple-DES or 3DES is an encryption protocol that provides stronger encryption than DES.
It is documented in Federal Information Processing Standards Publication 46-3
(http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=128014). 3DES is a block cipher that uses a three- step encryption process that is more secure than DES. A block cipher is an encryption algorithm that operates on a fixed size block of data.
AES-CBC 128, 192, and 256 -
The AES in Cipher Block Chaining mode (AES-CBC) encryption algorithms are part of the
NSA Suite B and are documented in RFC 3602
(http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=127990). AES is documented in Federal Information
Processing Standards Publication 197 (http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=127986). The
AES algorithm is a symmetric block cipher that can encrypt and decrypt information in data blocks of 128 bits, using cipher keys with lengths of 128, 192, and 256 bits. Longer key lengths provide better security at the cost of CPU performance due to the more intensive computational requirements. Cipher block chaining (CBC) is used to hide patterns of identical blocks of data within a packet. An initialization vector (an initial random number) is used as the first random block to encrypt and decrypt a block of data. Different random blocks are used in conjunction with the secret key to encrypt each successive block. This ensures that identical sets of unsecured data (plaintext) result in unique, encrypted data blocks.
AES-GCM 128, 192, and 256 -
AES-GCM is both an integrity and encryption algorithm and is described in the Integrity algorithms section.
Question 14
A company has client computers that run Windows 8.1. The company uses Windows
BitLocker Drive Encryption with the data-only option o all client computers.
You need to remove data fragments that exist in the free space on the local computer disk drives, without affecting current user data.
Which command should you run on the computers?
- A. BdeHdCfg
- B. diskpart
- C. chkdsk
- D. manage-bde
Answer : D
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj647761.aspx
Manage-bde WipeFreeSpace|-w [<Drive>] [-Cancel] [-computername<Name>] [{-?|/?}] [{- help|-h}]
Wipes the free space on the volume removing any data fragments that may have existed in the space. Running this command on a volume that was encrypted using the Used Space
Only encryption method provides the same level of protection as the Full Volume
Encryption encryption method.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ff829850.aspx
Bdehdcfg -
Prepares a hard drive with the partitions necessary for BitLocker Drive Encryption
Question 15
A company has an Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) domain. All client computers run Windows 8.1.
You need to minimize the amount of Trusted Platform Module (TPM) authorization information that is stored in the registry.
What should you do?
- A. Enable Platform Configuration Register indices (PCRs) 0, 2, 4, and 11 for the Configure TPM validation profile for native UEFI firmware configuration policy setting.
- B. Create a Group Policy object (GPO) that disables the Configure the level of TPM owner authorization information available to operating system policy setting.
- C. Create a Group Policy object (GPO) that sets the Configure the level of TPM owner authorization information available to operating system policy setting to None.
- D. Create a Group Policy object (GPO) that enables the Turn on TPM Local Encryption policy setting.
Answer : C
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj679889.aspx#BKMK_tpmgp_oauthos
Configure the level of TPM owner authorization information available to the operating system
This policy setting configures how much of the TPM owner authorization information is stored in the registry of the local computer. Depending on the amount of TPM owner authorization information that is stored locally, the Windows operating system and TPM- based applications can perform certain actions in the TPM that require TPM owner authorization without requiring the user to enter the TPM owner password.
There are three TPM owner authentication settings that are managed by the Windows operating system. You can choose a value of Full, Delegate, or None.
Full - This setting stores the full TPM owner authorization, the TPM administrative delegation blob, and the TPM user delegation blob in the local registry. With this setting, you can use the TPM without requiring remote or external storage of the TPM owner authorization value. This setting is appropriate for scenarios that do not require you to reset the TPM anti-hammering logic or change the TPM owner authorization value. Some TPM- based applications may require that this setting is changed before features that depend on the TPM anti-hammering logic can be used.
Delegated - This setting stores only the TPM administrative delegation blob and the TPM user delegation blob in the local registry. This setting is appropriate for use with TPM- based applications that depend on the TPM antihammering logic. When you use this setting, we recommend using external or remote storage for the full TPM owner authorization valuefor example, backing up the value in Active Directory Domain
Services (AD DS).
None - This setting provides compatibility with previous operating systems and applications. You can also use it for scenarios when TPM owner authorization cannot be stored locally. Using this setting might cause issues with some TPM-based applications.
Further Information:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc770660.aspx
Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) can be used to store Trusted Platform Module
(TPM) recovery information.
There is only one TPM owner password per computer; therefore, the hash of the TPM owner password is stored as an attribute of the computer object in AD DS. The attribute has the common name (CN) of ms-TPM-OwnerInformation. http://www.group-policy.com/ref/policy/2859/Configure_TPM_platform_validation_profile
Configure TPM platform validation profile
This policy setting allows you to configure how the computer's Trusted Platform Module
(TPM) security hardware secures the BitLocker encryption key. This policy setting does not apply if the computer does not have a compatible TPM or if BitLocker has already been turned on with TPM protection.
If you enable this policy setting before turning on BitLocker, you can configure the boot components that the TPM will validate before unlocking access to th