Developing Microsoft SQL Server 2012/2014 Databases v1.0
Question 1
Scenario 3 -
Application Information -
You have two servers named SQL1 and SQL2. SQL1 has SQL Server 2012 Enterprise installed.
SQL2 has SQL Server 2008 Standard installed.
You have an application that is used to manage employees and office space. Users report that the application has many errors and is very slow.
You are updating the application to resolve the issues. You plan to create a new database on SQL1 to support the application. The script that you plan to use to create the tables for the new database is shown in Tables.sql. The script that you plan to use to create the stored procedures for the new database is shown in
StoredProcedures.sql. The script that you plan to use to create the indexes for the new database is shown in Indexes.sql. A database named DB2 resides on
SQL2. DB2 has a table named EmployeeAudit that will audit changes to a table named Employees.
A stored procedure named usp_UpdateEmployeeName will be executed only by other stored procedures. The stored procedures executing usp_UpdateEmp!oyeeName will always handle transactions.
A stored procedure named usp_SelectEmployeesByName will be used to retrieve the names of employees. Usp_SelectEmployeesByName can read uncommitted data. A stored procedure named usp_GetFutureOfficeAssignments will be used to retrieve office assignments that will occur in the future.
StoredProcedures.sql -
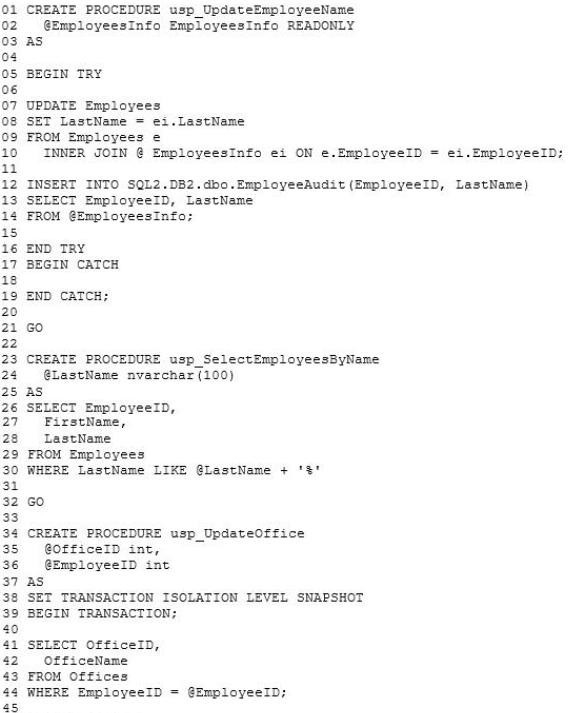
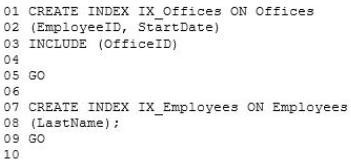
Indexes.sql -
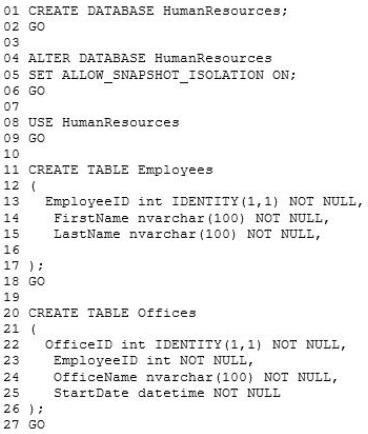
Tables.sql -
You need to add a new column named Confirmed to the Employees table.
The Confirmed column has the following requirements:
-> It must have a default value of TRUE.
-> It must minimize the amount of disk space used.
Which Transact-SQL statement should you run?
- A. ALTER TABLE Employees ADD Confirmed but DEFAULT 0;
- B. ALTER TABLE Employees ADD Confirmed but DEFAULT 1;
- C. ALTER TABLE Employees ADD Confirmed nchar(1) DEFAULT '1';
- D. ALTER TABLE Employees ADD Confirmed nchar(1) DEFAULT '0';
Answer : C
Topic 4, Scenario 4 -
Question 2
Scenario 4 -
Application Information -
You are a database administrator for a manufacturing company.
You have an application that stores product data. The data will be converted to technical diagrams for the manufacturing process.
The product details are stored in XML format. Each XML must contain only one product that has a root element named Product. A schema named
Production.ProductSchema has been created for the products xml.
You develop a Microsoft .NET Framework assembly named ProcessProducts.dll that will be used to convert the XML files to diagrams. The diagrams will be stored in the database as images. ProcessProducts.dll contains one class named ProcessProduct that has a method name of Convert(). ProcessProducts.dll was created by using a source code file named ProcessProduct.cs.
All of the files are located in C:\Products\.
The application has several performance and security issues. You will create a new database named ProductsDB on a new server that has SQL Server 2014 installed. ProductsDB will support the application.
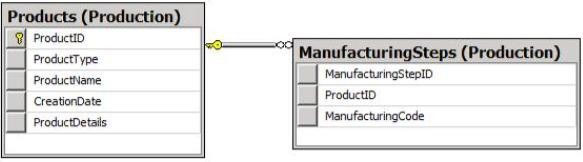
The following graphic shows the planned tables for ProductsDB:
You will also add a sequence named Production.ProductID_Seq.
You plan to create two certificates named DBCert and ProductsCert. You will create ProductsCert in master. You will create DBCert in ProductsDB.
You have an application that executes dynamic T-SQL statements against ProductsDB. A sample of the queries generated by the application appears in
Dynamic.sql.
Application Requirements -
The planned database has the following requirements:
All tables must be disk-based
All stored procedures must be signed.
The amount of disk space must be minimized.
Administrative effort must be minimized at all times.
The original product details must be stored in the database.
An XML schema must be used to validate the product details.
The assembly must be accessible by using T-SQL commands.
A table-valued function will be created to search products by type.
Backups must be protected by using the highest level of encryption.
Dynamic T-SQL statements must be converted to stored procedures.
Indexes must be optimized periodically based on their fragmentation.
Manufacturing steps stored in the ManufacturingSteps table must refer to a product by the same identifier used by the Products table.
ProductDetails_Insert.sql -

Product, xml -
All product types are 11 digits. The first five digits of the product id reference the category of the product and the remaining six digits are the subcategory of the product.
The following is a sample customer invoice in XML format:
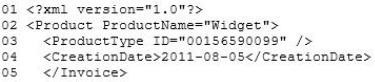
ProductsByProductType.sql -

Dynamic.sql -

Category FromType.sql -
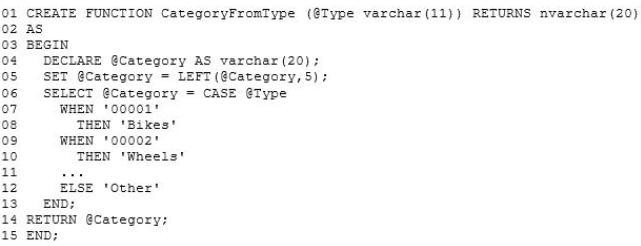
IndexManagement.sql -

An administrator provides a digital certificate named ServerCert.
You need to implement Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) on ProductsDB.
Which code segment should you use?
- A. USE PRODUCTSDB; GO CREATE DATABASE ENCRYPTION KEY WITH ALGORITHM = TRIPLE_DES_3KEY ENCRYPTION BY SERVER CERTIFICATE DBCERT; GO ALTER DATABASE PRODUCTSDB SET ENCRYPTION ON; GO
- B. USE PRODUCTSDB; GO CREATE DATABASE ENCRYPTION KEY WITH ALGORITHM = TRIPLE_DES_3KEY ENCRYPTION BY SERVER CERTIFICATE PRODUCTSCERT; GO ALTER DATABASE PRODUCTSDB SET ENCRYPTION ON; GO
- C. USE PRODUCTSDB; GO CREATE DATABASE ENCRYPTION KEY WITH ALGORITHM = AES_256 ENCRYPTION BY SERVER CERTIFICATE PRODUCTSCERT; GO ALTER DATABASE PRODUCTSDB SET ENCRYPTION ON; GO
- D. USE PRODUCTSDB; GO CREATE DATABASE ENCRYPTION KEY WITH ALGORITHM = AES_256 ENCRYPTION BY SERVER CERTIFICATE DBCERT; GO ALTER DATABASE PRODUCTSDB SET ENCRYPTION ON; GO
Answer : C
Explanation:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb934049.aspx
Question 3
Scenario 4 -
Application Information -
You are a database administrator for a manufacturing company.
You have an application that stores product data. The data will be converted to technical diagrams for the manufacturing process.
The product details are stored in XML format. Each XML must contain only one product that has a root element named Product. A schema named
Production.ProductSchema has been created for the products xml.
You develop a Microsoft .NET Framework assembly named ProcessProducts.dll that will be used to convert the XML files to diagrams. The diagrams will be stored in the database as images. ProcessProducts.dll contains one class named ProcessProduct that has a method name of Convert(). ProcessProducts.dll was created by using a source code file named ProcessProduct.cs.
All of the files are located in C:\Products\.
The application has several performance and security issues. You will create a new database named ProductsDB on a new server that has SQL Server 2014 installed. ProductsDB will support the application.
The following graphic shows the planned tables for ProductsDB:

You will also add a sequence named Production.ProductID_Seq.
You plan to create two certificates named DBCert and ProductsCert. You will create ProductsCert in master. You will create DBCert in ProductsDB.
You have an application that executes dynamic T-SQL statements against ProductsDB. A sample of the queries generated by the application appears in
Dynamic.sql.
Application Requirements -
The planned database has the following requirements:
All tables must be disk-based
All stored procedures must be signed.
The amount of disk space must be minimized.
Administrative effort must be minimized at all times.
The original product details must be stored in the database.
An XML schema must be used to validate the product details.
The assembly must be accessible by using T-SQL commands.
A table-valued function will be created to search products by type.
Backups must be protected by using the highest level of encryption.
Dynamic T-SQL statements must be converted to stored procedures.
Indexes must be optimized periodically based on their fragmentation.
Manufacturing steps stored in the ManufacturingSteps table must refer to a product by the same identifier used by the Products table.
ProductDetails_Insert.sql -

Product, xml -
All product types are 11 digits. The first five digits of the product id reference the category of the product and the remaining six digits are the subcategory of the product.
The following is a sample customer invoice in XML format:

ProductsByProductType.sql -

Dynamic.sql -

Category FromType.sql -

IndexManagement.sql -

You execute IndexManagement.sql and you receive the following error message: "Msg 512, Level 16, State 1, Line 12
Subquery returned more than 1 value. This is not permitted when the subquery follows =, != ,<, <= , >, > = or when the subquery is used as an expression."
You need to ensure that IndexManagement.sql executes properly.
Which WHILE statement should you use at line 18?
- A. WHILE SUM(@RowNumber) < (SELECT @counter FROM @indextable)
- B. WHILE @counter < (SELECT SUM(RowNumber) FROM @indextable)
- C. WHILE COUNT(@RowNumber) < (SELECT @counter FROM @indextable)
- D. WHILE @counter < (SELECT COUNT(RowNumber) FROM @indextable)
Answer : D
Question 4
Scenario 4 -
Application Information -
You are a database administrator for a manufacturing company.
You have an application that stores product data. The data will be converted to technical diagrams for the manufacturing process.
The product details are stored in XML format. Each XML must contain only one product that has a root element named Product. A schema named
Production.ProductSchema has been created for the products xml.
You develop a Microsoft .NET Framework assembly named ProcessProducts.dll that will be used to convert the XML files to diagrams. The diagrams will be stored in the database as images. ProcessProducts.dll contains one class named ProcessProduct that has a method name of Convert(). ProcessProducts.dll was created by using a source code file named ProcessProduct.cs.
All of the files are located in C:\Products\.
The application has several performance and security issues. You will create a new database named ProductsDB on a new server that has SQL Server 2014 installed. ProductsDB will support the application.
The following graphic shows the planned tables for ProductsDB:

You will also add a sequence named Production.ProductID_Seq.
You plan to create two certificates named DBCert and ProductsCert. You will create ProductsCert in master. You will create DBCert in ProductsDB.
You have an application that executes dynamic T-SQL statements against ProductsDB. A sample of the queries generated by the application appears in
Dynamic.sql.
Application Requirements -
The planned database has the following requirements:
All tables must be disk-based
All stored procedures must be signed.
The amount of disk space must be minimized.
Administrative effort must be minimized at all times.
The original product details must be stored in the database.
An XML schema must be used to validate the product details.
The assembly must be accessible by using T-SQL commands.
A table-valued function will be created to search products by type.
Backups must be protected by using the highest level of encryption.
Dynamic T-SQL statements must be converted to stored procedures.
Indexes must be optimized periodically based on their fragmentation.
Manufacturing steps stored in the ManufacturingSteps table must refer to a product by the same identifier used by the Products table.
ProductDetails_Insert.sql -

Product, xml -
All product types are 11 digits. The first five digits of the product id reference the category of the product and the remaining six digits are the subcategory of the product.
The following is a sample customer invoice in XML format:

ProductsByProductType.sql -

Dynamic.sql -

Category FromType.sql -

IndexManagement.sql -

You are planning the ManufacturingSteps table.
You need to define the ProductID column in the CREATE TABLE statement.
Which code segment should you use?

- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
- D. Option D
Answer : B
References:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms189049.aspx
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms179610.aspx
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ff878370.aspx
Question 5
Scenario 4 -
Application Information -
You are a database administrator for a manufacturing company.
You have an application that stores product data. The data will be converted to technical diagrams for the manufacturing process.
The product details are stored in XML format. Each XML must contain only one product that has a root element named Product. A schema named
Production.ProductSchema has been created for the products xml.
You develop a Microsoft .NET Framework assembly named ProcessProducts.dll that will be used to convert the XML files to diagrams. The diagrams will be stored in the database as images. ProcessProducts.dll contains one class named ProcessProduct that has a method name of Convert(). ProcessProducts.dll was created by using a source code file named ProcessProduct.cs.
All of the files are located in C:\Products\.
The application has several performance and security issues. You will create a new database named ProductsDB on a new server that has SQL Server 2014 installed. ProductsDB will support the application.
The following graphic shows the planned tables for ProductsDB:

You will also add a sequence named Production.ProductID_Seq.
You plan to create two certificates named DBCert and ProductsCert. You will create ProductsCert in master. You will create DBCert in ProductsDB.
You have an application that executes dynamic T-SQL statements against ProductsDB. A sample of the queries generated by the application appears in
Dynamic.sql.
Application Requirements -
The planned database has the following requirements:
All tables must be disk-based
All stored procedures must be signed.
The amount of disk space must be minimized.
Administrative effort must be minimized at all times.
The original product details must be stored in the database.
An XML schema must be used to validate the product details.
The assembly must be accessible by using T-SQL commands.
A table-valued function will be created to search products by type.
Backups must be protected by using the highest level of encryption.
Dynamic T-SQL statements must be converted to stored procedures.
Indexes must be optimized periodically based on their fragmentation.
Manufacturing steps stored in the ManufacturingSteps table must refer to a product by the same identifier used by the Products table.
ProductDetails_Insert.sql -

Product, xml -
All product types are 11 digits. The first five digits of the product id reference the category of the product and the remaining six digits are the subcategory of the product.
The following is a sample customer invoice in XML format:

ProductsByProductType.sql -

Dynamic.sql -

Category FromType.sql -

IndexManagement.sql -

You are testing disaster recovery procedures.
When you attempt to restore ProductsDB to another server, you receive the following error message: "Msg
33111, Level 16, State 3, Line 5
Cannot find server certificate with thumbprint ' 0x9D876A3468B911ElBA4CFCBF4724019B\ Msg 3013, Level 16, State 1, Line 5
RESTORE DATABASE is terminating abnormally."
You need to ensure that you can restore ProductsDB to another server.
Which code segment should you execute on the other server?
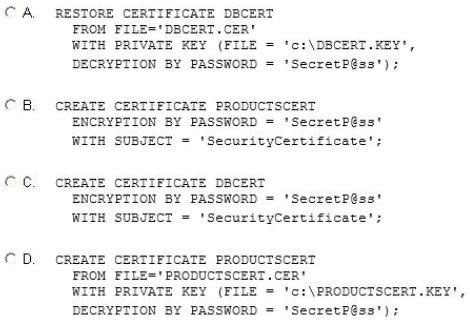
- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
- D. Option D
Answer : D
Question 6
Scenario 4 -
Application Information -
You are a database administrator for a manufacturing company.
You have an application that stores product data. The data will be converted to technical diagrams for the manufacturing process.
The product details are stored in XML format. Each XML must contain only one product that has a root element named Product. A schema named
Production.ProductSchema has been created for the products xml.
You develop a Microsoft .NET Framework assembly named ProcessProducts.dll that will be used to convert the XML files to diagrams. The diagrams will be stored in the database as images. ProcessProducts.dll contains one class named ProcessProduct that has a method name of Convert(). ProcessProducts.dll was created by using a source code file named ProcessProduct.cs.
All of the files are located in C:\Products\.
The application has several performance and security issues. You will create a new database named ProductsDB on a new server that has SQL Server 2014 installed. ProductsDB will support the application.
The following graphic shows the planned tables for ProductsDB:

You will also add a sequence named Production.ProductID_Seq.
You plan to create two certificates named DBCert and ProductsCert. You will create ProductsCert in master. You will create DBCert in ProductsDB.
You have an application that executes dynamic T-SQL statements against ProductsDB. A sample of the queries generated by the application appears in
Dynamic.sql.
Application Requirements -
The planned database has the following requirements:
All tables must be disk-based
All stored procedures must be signed.
The amount of disk space must be minimized.
Administrative effort must be minimized at all times.
The original product details must be stored in the database.
An XML schema must be used to validate the product details.
The assembly must be accessible by using T-SQL commands.
A table-valued function will be created to search products by type.
Backups must be protected by using the highest level of encryption.
Dynamic T-SQL statements must be converted to stored procedures.
Indexes must be optimized periodically based on their fragmentation.
Manufacturing steps stored in the ManufacturingSteps table must refer to a product by the same identifier used by the Products table.
ProductDetails_Insert.sql -

Product, xml -
All product types are 11 digits. The first five digits of the product id reference the category of the product and the remaining six digits are the subcategory of the product.
The following is a sample customer invoice in XML format:

ProductsByProductType.sql -

Dynamic.sql -

Category FromType.sql -

IndexManagement.sql -

You need to prepare the database to use the .NET Framework ProcessProducts component.
Which code segments should you execute? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution.
Choose all that apply.)

- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
- D. Option D
- E. Option E
- F. Option F
- G. Option G
Answer : ACDE
References:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms131048.aspx
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms131052.aspx
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms189524.aspx
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms345106.aspx
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms131107.aspx
Question 7
Scenario 4 -
Application Information -
You are a database administrator for a manufacturing company.
You have an application that stores product data. The data will be converted to technical diagrams for the manufacturing process.
The product details are stored in XML format. Each XML must contain only one product that has a root element named Product. A schema named
Production.ProductSchema has been created for the products xml.
You develop a Microsoft .NET Framework assembly named ProcessProducts.dll that will be used to convert the XML files to diagrams. The diagrams will be stored in the database as images. ProcessProducts.dll contains one class named ProcessProduct that has a method name of Convert(). ProcessProducts.dll was created by using a source code file named ProcessProduct.cs.
All of the files are located in C:\Products\.
The application has several performance and security issues. You will create a new database named ProductsDB on a new server that has SQL Server 2014 installed. ProductsDB will support the application.
The following graphic shows the planned tables for ProductsDB:

You will also add a sequence named Production.ProductID_Seq.
You plan to create two certificates named DBCert and ProductsCert. You will create ProductsCert in master. You will create DBCert in ProductsDB.
You have an application that executes dynamic T-SQL statements against ProductsDB. A sample of the queries generated by the application appears in
Dynamic.sql.
Application Requirements -
The planned database has the following requirements:
All tables must be disk-based
All stored procedures must be signed.
The amount of disk space must be minimized.
Administrative effort must be minimized at all times.
The original product details must be stored in the database.
An XML schema must be used to validate the product details.
The assembly must be accessible by using T-SQL commands.
A table-valued function will be created to search products by type.
Backups must be protected by using the highest level of encryption.
Dynamic T-SQL statements must be converted to stored procedures.
Indexes must be optimized periodically based on their fragmentation.
Manufacturing steps stored in the ManufacturingSteps table must refer to a product by the same identifier used by the Products table.
ProductDetails_Insert.sql -

Product, xml -
All product types are 11 digits. The first five digits of the product id reference the category of the product and the remaining six digits are the subcategory of the product.
The following is a sample customer invoice in XML format:

ProductsByProductType.sql -

Dynamic.sql -

Category FromType.sql -

IndexManagement.sql -

While testing the CategoryFromType function, you discover that the function is returning 'Other'. You need to update CategoryFromType to return the category name.
Which line of code should you modify in CategoryFromType.sql?
- A. 04
- B. 05
- C. 12
- D. 14
Answer : B
Question 8
Scenario 4 -
Application Information -
You are a database administrator for a manufacturing company.
You have an application that stores product data. The data will be converted to technical diagrams for the manufacturing process.
The product details are stored in XML format. Each XML must contain only one product that has a root element named Product. A schema named
Production.ProductSchema has been created for the products xml.
You develop a Microsoft .NET Framework assembly named ProcessProducts.dll that will be used to convert the XML files to diagrams. The diagrams will be stored in the database as images. ProcessProducts.dll contains one class named ProcessProduct that has a method name of Convert(). ProcessProducts.dll was created by using a source code file named ProcessProduct.cs.
All of the files are located in C:\Products\.
The application has several performance and security issues. You will create a new database named ProductsDB on a new server that has SQL Server 2014 installed. ProductsDB will support the application.
The following graphic shows the planned tables for ProductsDB:

You will also add a sequence named Production.ProductID_Seq.
You plan to create two certificates named DBCert and ProductsCert. You will create ProductsCert in master. You will create DBCert in ProductsDB.
You have an application that executes dynamic T-SQL statements against ProductsDB. A sample of the queries generated by the application appears in
Dynamic.sql.
Application Requirements -
The planned database has the following requirements:
All tables must be disk-based
All stored procedures must be signed.
The amount of disk space must be minimized.
Administrative effort must be minimized at all times.
The original product details must be stored in the database.
An XML schema must be used to validate the product details.
The assembly must be accessible by using T-SQL commands.
A table-valued function will be created to search products by type.
Backups must be protected by using the highest level of encryption.
Dynamic T-SQL statements must be converted to stored procedures.
Indexes must be optimized periodically based on their fragmentation.
Manufacturing steps stored in the ManufacturingSteps table must refer to a product by the same identifier used by the Products table.
ProductDetails_Insert.sql -

Product, xml -
All product types are 11 digits. The first five digits of the product id reference the category of the product and the remaining six digits are the subcategory of the product.
The following is a sample customer invoice in XML format:

ProductsByProductType.sql -

Dynamic.sql -

Category FromType.sql -

IndexManagement.sql -

Which data type should you use for ProductType?
- A. varchar(11)
- B. nvarchar(11)
- C. char(11)
- D. bigint
Answer : C
Question 9
Scenario 4 -
Application Information -
You are a database administrator for a manufacturing company.
You have an application that stores product data. The data will be converted to technical diagrams for the manufacturing process.
The product details are stored in XML format. Each XML must contain only one product that has a root element named Product. A schema named
Production.ProductSchema has been created for the products xml.
You develop a Microsoft .NET Framework assembly named ProcessProducts.dll that will be used to convert the XML files to diagrams. The diagrams will be stored in the database as images. ProcessProducts.dll contains one class named ProcessProduct that has a method name of Convert(). ProcessProducts.dll was created by using a source code file named ProcessProduct.cs.
All of the files are located in C:\Products\.
The application has several performance and security issues. You will create a new database named ProductsDB on a new server that has SQL Server 2014 installed. ProductsDB will support the application.
The following graphic shows the planned tables for ProductsDB:

You will also add a sequence named Production.ProductID_Seq.
You plan to create two certificates named DBCert and ProductsCert. You will create ProductsCert in master. You will create DBCert in ProductsDB.
You have an application that executes dynamic T-SQL statements against ProductsDB. A sample of the queries generated by the application appears in
Dynamic.sql.
Application Requirements -
The planned database has the following requirements:
All tables must be disk-based
All stored procedures must be signed.
The amount of disk space must be minimized.
Administrative effort must be minimized at all times.
The original product details must be stored in the database.
An XML schema must be used to validate the product details.
The assembly must be accessible by using T-SQL commands.
A table-valued function will be created to search products by type.
Backups must be protected by using the highest level of encryption.
Dynamic T-SQL statements must be converted to stored procedures.
Indexes must be optimized periodically based on their fragmentation.
Manufacturing steps stored in the ManufacturingSteps table must refer to a product by the same identifier used by the Products table.
ProductDetails_Insert.sql -

Product, xml -
All product types are 11 digits. The first five digits of the product id reference the category of the product and the remaining six digits are the subcategory of the product.
The following is a sample customer invoice in XML format:

ProductsByProductType.sql -

Dynamic.sql -

Category FromType.sql -

IndexManagement.sql -

Which code segment should you use to define the ProductDetails column?
- A. ProductDetails xml (DOCUMENT Production.ProductDetailsSchema) NULL
- B. ProductDetails xml NULL
- C. ProductDetails xml (CONTENT Production.ProductDetailsSchema) NULL
- D. ProductDetails varchar(MAX) NULL
Answer : D
Question 10
Scenario 4 -
Application Information -
You are a database administrator for a manufacturing company.
You have an application that stores product data. The data will be converted to technical diagrams for the manufacturing process.
The product details are stored in XML format. Each XML must contain only one product that has a root element named Product. A schema named
Production.ProductSchema has been created for the products xml.
You develop a Microsoft .NET Framework assembly named ProcessProducts.dll that will be used to convert the XML files to diagrams. The diagrams will be stored in the database as images. ProcessProducts.dll contains one class named ProcessProduct that has a method name of Convert(). ProcessProducts.dll was created by using a source code file named ProcessProduct.cs.
All of the files are located in C:\Products\.
The application has several performance and security issues. You will create a new database named ProductsDB on a new server that has SQL Server 2014 installed. ProductsDB will support the application.
The following graphic shows the planned tables for ProductsDB:

You will also add a sequence named Production.ProductID_Seq.
You plan to create two certificates named DBCert and ProductsCert. You will create ProductsCert in master. You will create DBCert in ProductsDB.
You have an application that executes dynamic T-SQL statements against ProductsDB. A sample of the queries generated by the application appears in
Dynamic.sql.
Application Requirements -
The planned database has the following requirements:
All tables must be disk-based
All stored procedures must be signed.
The amount of disk space must be minimized.
Administrative effort must be minimized at all times.
The original product details must be stored in the database.
An XML schema must be used to validate the product details.
The assembly must be accessible by using T-SQL commands.
A table-valued function will be created to search products by type.
Backups must be protected by using the highest level of encryption.
Dynamic T-SQL statements must be converted to stored procedures.
Indexes must be optimized periodically based on their fragmentation.
Manufacturing steps stored in the ManufacturingSteps table must refer to a product by the same identifier used by the Products table.
ProductDetails_Insert.sql -

Product, xml -
All product types are 11 digits. The first five digits of the product id reference the category of the product and the remaining six digits are the subcategory of the product.
The following is a sample customer invoice in XML format:

ProductsByProductType.sql -

Dynamic.sql -

Category FromType.sql -

IndexManagement.sql -

You need to modify Production.ProductDetails_Insert to comply with the application requirements.
Which code segment should you execute?

- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
- D. Option D
Answer : C
Explanation:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb669102.aspx
Question 11
Scenario 4 -
Application Information -
You are a database administrator for a manufacturing company.
You have an application that stores product data. The data will be converted to technical diagrams for the manufacturing process.
The product details are stored in XML format. Each XML must contain only one product that has a root element named Product. A schema named
Production.ProductSchema has been created for the products xml.
You develop a Microsoft .NET Framework assembly named ProcessProducts.dll that will be used to convert the XML files to diagrams. The diagrams will be stored in the database as images. ProcessProducts.dll contains one class named ProcessProduct that has a method name of Convert(). ProcessProducts.dll was created by using a source code file named ProcessProduct.cs.
All of the files are located in C:\Products\.
The application has several performance and security issues. You will create a new database named ProductsDB on a new server that has SQL Server 2014 installed. ProductsDB will support the application.
The following graphic shows the planned tables for ProductsDB:

You will also add a sequence named Production.ProductID_Seq.
You plan to create two certificates named DBCert and ProductsCert. You will create ProductsCert in master. You will create DBCert in ProductsDB.
You have an application that executes dynamic T-SQL statements against ProductsDB. A sample of the queries generated by the application appears in
Dynamic.sql.
Application Requirements -
The planned database has the following requirements:
All tables must be disk-based
All stored procedures must be signed.
The amount of disk space must be minimized.
Administrative effort must be minimized at all times.
The original product details must be stored in the database.
An XML schema must be used to validate the product details.
The assembly must be accessible by using T-SQL commands.
A table-valued function will be created to search products by type.
Backups must be protected by using the highest level of encryption.
Dynamic T-SQL statements must be converted to stored procedures.
Indexes must be optimized periodically based on their fragmentation.
Manufacturing steps stored in the ManufacturingSteps table must refer to a product by the same identifier used by the Products table.
ProductDetails_Insert.sql -

Product, xml -
All product types are 11 digits. The first five digits of the product id reference the category of the product and the remaining six digits are the subcategory of the product.
The following is a sample customer invoice in XML format:

ProductsByProductType.sql -

Dynamic.sql -

Category FromType.sql -

IndexManagement.sql -

You need to create a function that will use a SELECT statement in ProductsByProductType.sql.
Which code segment should you use to complete the function?

- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
- D. Option D
Answer : B
Explanation:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms191320.aspx
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms186755.aspx
Question 12
Scenario 4 -
Application Information -
You are a database administrator for a manufacturing company.
You have an application that stores product data. The data will be converted to technical diagrams for the manufacturing process.
The product details are stored in XML format. Each XML must contain only one product that has a root element named Product. A schema named
Production.ProductSchema has been created for the products xml.
You develop a Microsoft .NET Framework assembly named ProcessProducts.dll that will be used to convert the XML files to diagrams. The diagrams will be stored in the database as images. ProcessProducts.dll contains one class named ProcessProduct that has a method name of Convert(). ProcessProducts.dll was created by using a source code file named ProcessProduct.cs.
All of the files are located in C:\Products\.
The application has several performance and security issues. You will create a new database named ProductsDB on a new server that has SQL Server 2014 installed. ProductsDB will support the application.
The following graphic shows the planned tables for ProductsDB:

You will also add a sequence named Production.ProductID_Seq.
You plan to create two certificates named DBCert and ProductsCert. You will create ProductsCert in master. You will create DBCert in ProductsDB.
You have an application that executes dynamic T-SQL statements against ProductsDB. A sample of the queries generated by the application appears in
Dynamic.sql.
Application Requirements -
The planned database has the following requirements:
All tables must be disk-based
All stored procedures must be signed.
The amount of disk space must be minimized.
Administrative effort must be minimized at all times.
The original product details must be stored in the database.
An XML schema must be used to validate the product details.
The assembly must be accessible by using T-SQL commands.
A table-valued function will be created to search products by type.
Backups must be protected by using the highest level of encryption.
Dynamic T-SQL statements must be converted to stored procedures.
Indexes must be optimized periodically based on their fragmentation.
Manufacturing steps stored in the ManufacturingSteps table must refer to a product by the same identifier used by the Products table.
ProductDetails_Insert.sql -

Product, xml -
All product types are 11 digits. The first five digits of the product id reference the category of the product and the remaining six digits are the subcategory of the product.
The following is a sample customer invoice in XML format:

ProductsByProductType.sql -

Dynamic.sql -

Category FromType.sql -

IndexManagement.sql -

You need to convert the functionality of Dynamic.sql to use a stored procedure.
Which Transact SQL statement should you add to the stored procedure contain?
- A. CREATE PROC Production.ProductsAfterDate (@ProductID AS varchar(11), @CreationDate AS date) AS ...
- B. CREATE PROC Production.ProductsAfterDate( @sqlstring AS nvarchar(1000)) AS ...
- C. CREATE PROC Production.ProductsAfterDate( @sqlstring AS nvarchar(1000), OUTPUT @ProductID AS varchar(11), OUTPUT @CreationDate AS date) AS ...
- D. CREATE PROC Production.ProductsAfterDate( @sqlstring AS nvarchar(1000), @ProductID AS varchar(11), @CreationDate AS date) AS ...
Answer : C
Explanation:
@sqlstring, @ProductID, and @CreationData need to be declared as parameters. @ProductID, and @CreationData should be output parameters.
Topic 5, Litware, Inc -
Question 13
Litware, Inc -
General Overview -
General Overview -
You are a database developer for a company named Litware, Inc. Litware has a main office in Miami.
Litware has a job posting web application named WebApp1. WebApp1 uses a database named DB1. DB1 is hosted on a server named Server1. The database design of DB1 is shown in the exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.)
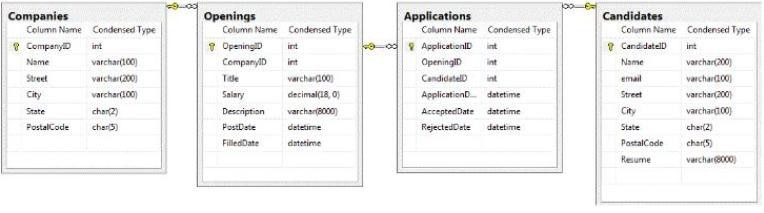
WebApp1 allows a user to log on as a job poster or a job seeker. Candidates can search for job openings based on keywords, apply to an opening, view their application, and load their resume in Microsoft Word format. Companies can add a job opening, view the list of candidates who applied to an opening, and mark an application as denied.
Users and Roles -
DB1 has five database users named Company, CompanyWeb, Candidate, CandidateWeb, and Administrator.
DB1 has three user-defined database roles. The roles are configured as shown in the following table.
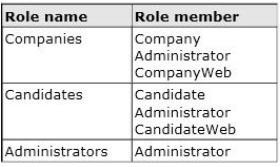
Keyword Search -
The keyword searches for the job openings are performed by using the following stored procedure named usp_GetOpenings:

Opening Update -
Updates to the Openings table are performed by using the following stored procedure named usp_UpdateOpening:

Problems and Reported Issues -
Concurrency Problems -
You discover that deadlocks frequently occur.
You identify that a stored procedure named usp_AcceptCandidate and a stored procedure named usp_UpdateCandidate generate deadlocks. The following is the code for usp_AcceptCandidate:
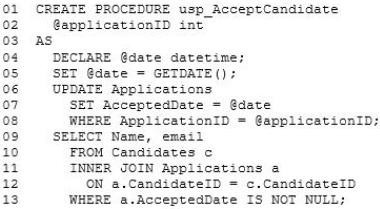
Salary Query Issues -
Users report that when they perform a search for job openings without specifying a minimum salary, only job openings that specify a minimum salary are displayed.
Log File Growth Issues -
The current log file for DB1 grows constantly. The log file fails to shrink even when the daily SQL Server Agent Shrink Database task runs.
Performance Issues -
You discover that a stored procedure named usp_ExportOpenings takes a long time to run and executes a table scan when it runs.
You also discover that the usp_GetOpenings stored procedure takes a long time to run and that the non-clustered index on the Description column is not being used.
Page Split Issues -
On DB1, many page splits per second spike every few minutes.
Requirements -
Security and Application Requirements
Litware identifies the following security and application requirements:
Only the Administrator, Company, and CompanyWeb database users must be able to execute the usp_UpdateOpening stored procedure.
Changes made to the database must not affect WebApp1.
Locking Requirements -
Litware identifies the following locking requirements:
The usp_GetOpenings stored procedure must not be blocked by the usp_UpdateOpening stored procedure.
If a row is locked in the Openings table, usp_GetOpenings must retrieve the latest version of the row, even if the row was not committed yet.
Integration Requirements -
Litware exports its job openings to an external company as XML data. The XML data uses the following format:

A stored procedure named usp_ExportOpenings will be used to generate the XML data. The following is the code for usp_ExportOpenings:
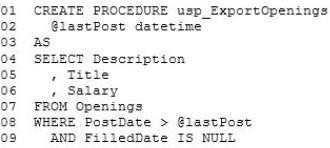
The stored procedure will be executed by a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) package named Package1.
The XML data will be written to a secured folder named Folder1. Only a dedicated Active Directory account named Account1 is assigned the permissions to read from or write to Folder1.
Refactoring Requirements -
Litware identifies the following refactoring requirements:
New code must be written by reusing the following query:
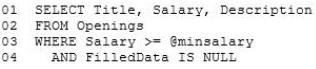
The results from the query must be able to be joined to other queries.
Upload Requirements -
Litware requires users to upload their job experience in a Word file by using WebApp1. WebApp1 will send the Word file to DB1 as a stream of bytes. DB1 will then convert the Word file to text before the contents of the Word file is saved to the Candidates table.
A database developer creates an assembly named Conversions that contains the following:
A class named Convert in the SqlConversions namespace
A method named ConvertToText in the Convert class that converts Word files to text
The ConvertToText method accepts a stream of bytes and returns text. The method is used in the following stored procedure:
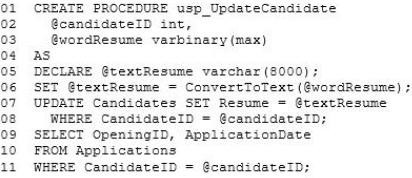
Job Application Requirements -
A candidate can only apply to each job opening once.
Data Recovery Requirements -
All changes to the database are performed by using stored procedures. WebApp1 generates a unique transaction ID for every stored procedure call that the application makes to the database.
If a server fails, you must be able to restore data to a specified transaction.
You need to design a solution that meets the refactoring requirements.
Which type of object should you include in the solution?
- A. A CLR stored procedure
- B. A scalar function
- C. A T-SQL stored procedure
- D. A table-valued function
Answer : D
Explanation:
From scenario: The results from the query must be able to be joined to other queries.
User-defined functions that return a table data type can be powerful alternatives to views. These functions are referred to as table-valued functions. A table-valued user-defined function can be used where table or view expressions are allowed in Transact-SQL queries. While views are limited to a single SELECT statement, user-defined functions can contain additional statements that allow more powerful logic than is possible in views.
A table-valued user-defined function can also replace stored procedures that return a single result set. The table returned by a user-defined function can be referenced in the FROM clause of a Transact-SQL statement, but stored procedures that return result sets cannot.
References:
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms191165(v=sql.105).aspx
Question 14
Litware, Inc -
General Overview -
General Overview -
You are a database developer for a company named Litware, Inc. Litware has a main office in Miami.
Litware has a job posting web application named WebApp1. WebApp1 uses a database named DB1. DB1 is hosted on a server named Server1. The database design of DB1 is shown in the exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.)

WebApp1 allows a user to log on as a job poster or a job seeker. Candidates can search for job openings based on keywords, apply to an opening, view their application, and load their resume in Microsoft Word format. Companies can add a job opening, view the list of candidates who applied to an opening, and mark an application as denied.
Users and Roles -
DB1 has five database users named Company, CompanyWeb, Candidate, CandidateWeb, and Administrator.
DB1 has three user-defined database roles. The roles are configured as shown in the following table.

Keyword Search -
The keyword searches for the job openings are performed by using the following stored procedure named usp_GetOpenings:

Opening Update -
Updates to the Openings table are performed by using the following stored procedure named usp_UpdateOpening:

Problems and Reported Issues -
Concurrency Problems -
You discover that deadlocks frequently occur.
You identify that a stored procedure named usp_AcceptCandidate and a stored procedure named usp_UpdateCandidate generate deadlocks. The following is the code for usp_AcceptCandidate:

Salary Query Issues -
Users report that when they perform a search for job openings without specifying a minimum salary, only job openings that specify a minimum salary are displayed.
Log File Growth Issues -
The current log file for DB1 grows constantly. The log file fails to shrink even when the daily SQL Server Agent Shrink Database task runs.
Performance Issues -
You discover that a stored procedure named usp_ExportOpenings takes a long time to run and executes a table scan when it runs.
You also discover that the usp_GetOpenings stored procedure takes a long time to run and that the non-clustered index on the Description column is not being used.
Page Split Issues -
On DB1, many page splits per second spike every few minutes.
Requirements -
Security and Application Requirements
Litware identifies the following security and application requirements:
Only the Administrator, Company, and CompanyWeb database users must be able to execute the usp_UpdateOpening stored procedure.
Changes made to the database must not affect WebApp1.
Locking Requirements -
Litware identifies the following locking requirements:
The usp_GetOpenings stored procedure must not be blocked by the usp_UpdateOpening stored procedure.
If a row is locked in the Openings table, usp_GetOpenings must retrieve the latest version of the row, even if the row was not committed yet.
Integration Requirements -
Litware exports its job openings to an external company as XML data. The XML data uses the following format:

A stored procedure named usp_ExportOpenings will be used to generate the XML data. The following is the code for usp_ExportOpenings:

The stored procedure will be executed by a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) package named Package1.
The XML data will be written to a secured folder named Folder1. Only a dedicated Active Directory account named Account1 is assigned the permissions to read from or write to Folder1.
Refactoring Requirements -
Litware identifies the following refactoring requirements:
New code must be written by reusing the following query:

The results from the query must be able to be joined to other queries.
Upload Requirements -
Litware requires users to upload their job experience in a Word file by using WebApp1. WebApp1 will send the Word file to DB1 as a stream of bytes. DB1 will then convert the Word file to text before the contents of the Word file is saved to the Candidates table.
A database developer creates an assembly named Conversions that contains the following:
A class named Convert in the SqlConversions namespace
A method named ConvertToText in the Convert class that converts Word files to text
The ConvertToText method accepts a stream of bytes and returns text. The method is used in the following stored procedure:

Job Application Requirements -
A candidate can only apply to each job opening once.
Data Recovery Requirements -
All changes to the database are performed by using stored procedures. WebApp1 generates a unique transaction ID for every stored procedure call that the application makes to the database.
If a server fails, you must be able to restore data to a specified transaction.
You need to create a script that automates the export of the XML data. The script must meet the integration requirements.
What should you include in the script?
- A. The CREATE SERVER ROLE command and the sp_reassign_proxy, sp_add_job, sp_add_jobstep, and sp_grant_login_to_proxy system stored procedures.
- B. The CREATE CREDENTIAL command and the sp_add_proxy, sp_add_job, sp_add_jobstep, and sp_grant_proxy_to_subsystem system stored procedures.
- C. The CREATE CREDENTIAL command and the sp_reassign_proxy, sp_add_job, sp_add_jobstep, and sp_grant_login_to_proxy system stored procedures.
- D. The CREATE SERVER ROLE command and the sp_add_proxy, sp_add_job, sp_add_jobstep, and sp_grant_proxy_to_subsystem system stored procedures.
Answer : B
Question 15
Litware, Inc -
General Overview -
General Overview -
You are a database developer for a company named Litware, Inc. Litware has a main office in Miami.
Litware has a job posting web application named WebApp1. WebApp1 uses a database named DB1. DB1 is hosted on a server named Server1. The database design of DB1 is shown in the exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.)

WebApp1 allows a user to log on as a job poster or a job seeker. Candidates can search for job openings based on keywords, apply to an opening, view their application, and load their resume in Microsoft Word format. Companies can add a job opening, view the list of candidates who applied to an opening, and mark an application as denied.
Users and Roles -
DB1 has five database users named Company, CompanyWeb, Candidate, CandidateWeb, and Administrator.
DB1 has three user-defined database roles. The roles are configured as shown in the following table.

Keyword Search -
The keyword searches for the job openings are performed by using the following stored procedure named usp_GetOpenings:

Opening Update -
Updates to the Openings table are performed by using the following stored procedure named usp_UpdateOpening:

Problems and Reported Issues -
Concurrency Problems -
You discover that deadlocks frequently occur.
You identify that a stored procedure named usp_AcceptCandidate and a stored procedure named usp_UpdateCandidate generate deadlocks. The following is the code for usp_AcceptCandidate:

Salary Query Issues -
Users report that when they perform a search for job openings without specifying a minimum salary, only job openings that specify a minimum salary are displayed.
Log File Growth Issues -
The current log file for DB1 grows constantly. The log file fails to shrink even when the daily SQL Server Agent Shrink Database task runs.
Performance Issues -
You discover that a stored procedure named usp_ExportOpenings takes a long time to run and executes a table scan when it runs.
You also discover that the usp_GetOpenings stored procedure takes a long time to run and that the non-clustered index on the Description column is not being used.
Page Split Issues -
On DB1, many page splits per second spike every few minutes.
Requirements -
Security and Application Requirements
Litware identifies the following security and application requirements:
Only the Administrator, Company, and CompanyWeb database users must be able to execute the usp_UpdateOpening stored procedure.
Changes made to the database must not affect WebApp1.
Locking Requirements -
Litware identifies the following locking requirements:
The usp_GetOpenings stored procedure must not be blocked by the usp_UpdateOpening stored procedure.
If a row is locked in the Openings table, usp_GetOpenings must retrieve the latest version of the row, even if the row was not committed yet.
Integration Requirements -
Litware exports its job openings to an external company as XML data. The XML data uses the following format:

A stored procedure named usp_ExportOpenings will be used to generate the XML data. The following is the code for usp_ExportOpenings:

The stored procedure will be executed by a SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) package named Package1.
The XML data will be written to a secured folder named Folder1. Only a dedicated Active Directory account named Account1 is assigned the permissions to read from or write to Folder1.
Refactoring Requirements -
Litware identifies the following refactoring requirements:
New code must be written by reusing the following query:

The results from the query must be able to be joined to other queries.
Upload Requirements -
Litware requires users to upload their job experience in a Word file by using WebApp1. WebApp1 will send the Word file to DB1 as a stream of bytes. DB1 will then convert the Word file to text before the contents of the Word file is saved to the Candidates table.
A database developer creates an assembly named Conversions that contains the following:
A class named Convert in the SqlConversions namespace
A method named ConvertToText in the Convert class that converts Word files to text
The ConvertToText method accepts a stream of bytes and returns text. The method is used in the following stored procedure:

Job Application Requirements -
A candidate can only apply to each job opening once.
Data Recovery Requirements -
All changes to the database are performed by using stored procedures. WebApp1 generates a unique transaction ID for every stored procedure call that the application makes to the database.
If a server fails, you must be able to restore data to a specified transaction.
You need to implement a solution that meets the security requirements.
Which statement should you execute?

- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
- D. Option D
Answer : A