CCIE SP Written v4.1 v1.0
Question 1
Which two BGP mechanisms solve the BGP full-mesh paradigm? (Choose two.)
- A. BGP link state
- B. MPLS VPN
- C. route reflectors
- D. hierarchical VPLS
- E. confederation
- F. route policy filtering
- G. community SOO
Answer : CE
Question 2
Two routers that are running MPLS and LDP have multiple links that than connect them to each other. An engineer wants to ensure that the label bindings are not flushed from the LIB if one of the links fails. Which configuration meets this requirement?
- A. thempls ldpautoconfigcommand
- B. thempls ipcommand on an MPLS TE tunnel
- C. thempls ldp synccommand under router process configuration mode
- D. thempls ldp discoverytargeted-hello accept command
Answer : D
Explanation:
Question 3
Drag and drop the service provider MPLS core component on the left onto the matching functionality on the right.
Select and Place:
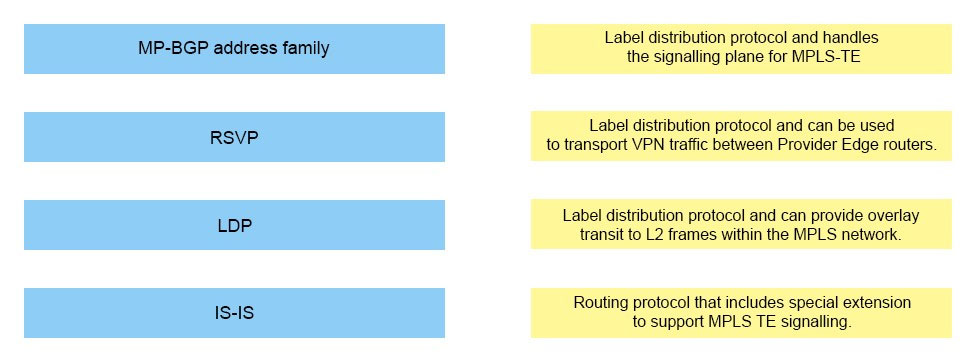
Answer : 
Question 4
Which statement is one specific characteristic of the BGP confederations implementation compared to the BGP route reflector implementation?
- A. BGP confederations allow the use of template sessions and template policies. A route reflector can only use peer groups.
- B. BGP confederations provide better redundancy. Route reflector clients can peer to only one cluster.
- C. The IBGP policies can differ internally within and between the subautonomous systems.
- D. BGP confederations are more scalable. A route reflector implementation still requires BGP confederations to eliminate the full mesh requirement.
Answer : C
Question 5
A service provider is in the process of providing Layer 2 and Layer 3 VPN services through a MPLS LDP-enabled backbone. With load increasing in the service provider domain, scalability become the most important. Based on the local label allocation filtering feature, which is the lower subset of prefixes must be selected to meet these requirements?
- A. RR, P, and PE loopbacks that are used as BGP next hop
- B. all/32 prefixes advertised in the IGP
- C. P and PE loopbacks that are used as BGP next hop
- D. CE loopbacks only that are used as BGP next hop
Answer : A
Explanation:
Question 6
A service provider offers four classes of service for MPLS VPN customer with the following IPP/EXP values: i. voice = 5 ii. video = 4 iii. priority data = 3 iv. best-effort data = 0
The service-provider also supports multicast VPN services in the priority data and best-effort classes. Multicast VPN is implemented as a draft-rosen profile. On a
P router, in the MPLS core, the ingress QoS policy-map must classify all incoming packets, so that different classes of traffic can be property handled in fabric queues and egress queues. All types of packets in the core network must be covered.
Which ingress classification offers the optimal performance and provides the minimum number of actions that match the service provider QoS requirements?
- A. class-map match-any VOICE match mpls experimental topmost 5 class-map match-any VIDEO match mpls experimental topmost 4 class-map match-any CONTROL match mpls experimental topmost 6 7 class-map match-any PRIORITY match mpls experimental topmost 3 ! policy-map INGRESS class VOICE set gos-group 5 class VIDEO set gos-group 4 class CONTROL set gos-group 6 class PRIORITYset gos-group 3 class class-default
- B. class-map match-any VOICE match mpls experimental topmost 5 match precedence ipv4 flash-override class-map match-any VIDEO match mpls experimental topmost 4 match precedence ipv4 critical class-map match-any CONTROL match precedence ipv4 internet network class-map match-any PRIORITY match mpls experimental topmost 3 match precedence ipv4 flash ! policy-map INGRESS class VOICE set gos-group 5class VIDEO set gos-group 4 class CONTROL set gos-group 6 class PRIORITYset gos-group 3 class class-defaul
- C. class-map match-any VOICE match mpls experimental topmost 5 class-map match-any VIDEO match mpls experimental topmost 4 class-map match-any CONTROL class-map match-any PRIORITY match mpls experimental topmost 3match precedence ipv4 flash ! policy-map INGRESS class VOICE setg os-group 5class VIDEO set gos-group 4 class CONTROL set gos-group 6 class PRIORITY set gos-group 3 class class-default
- D. class-map match-any VOICE match precedence ipv4 critical class-map match-any VIDEO match precedence ipv4 flash-override class-map match-any PRIOTIRY match mpls experimental topmost 3 match precedence ipv4 flash ! policy-map INGRESS class VOICE set qos-group 5 class VIDEO set qos-group 4 class PRIORITY set qos-group 3 class class-default
Answer : A
Explanation:
Question 7
A Layer 3 VPN customer opened a case that reports connectivity loss with remote sites. An operations engineer realized this connectivity loss happened after the
LDP label filtering was applied. What is the root cause of this issue?
- A. Labels were not allocated for the P loopbacks.
- B. Labels were not allocated for the P and PE physical interfaces.
- C. Labels were not allocated for the PE loopbacks.
- D. Labels were not allocated for the PE, P and RR physical interfaces.
- E. Labels were not allocated for the PE, P and RR loopbacks.
- F. Labels were not allocated for the CE loopbacks and physical interfaces.
Answer : E
Explanation:
Question 8
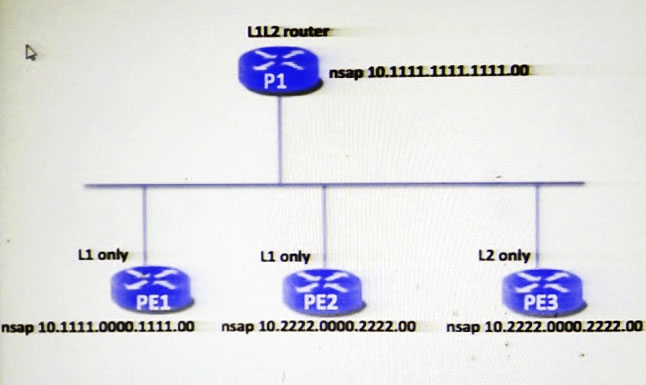
Refer to the exhibit. The P1 router is elected as the DIS on the broadcast link. Assuming that all the configurations are applied correctly, how many routers will establish IS-IS neighborship with P1 router on this broadcast link?
- A. 0
- B. 1
- C. 2
- D. 3
Answer : B
Explanation:
Question 9
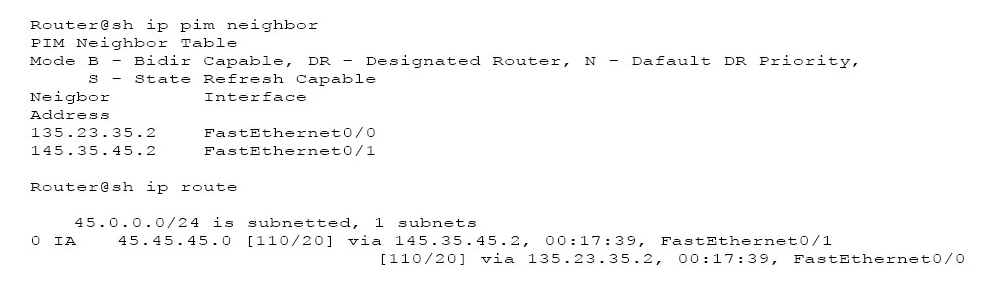
Refer to the exhibit. PIM sparse mode is implemented in the network. RPF succeeds under which condition?
- A. The RPF check succeeds for both PIM neighbors, and traffic load-balances across both neighbors.
- B. The RPF check succeeds for the next hop whose router ID is the highest.
- C. The RPF check succeeds for the highest DR priority for the PIM router.
- D. The RPF check succeeds for the highest interface IP address for the PIM router.
Answer : D
Explanation:
Question 10
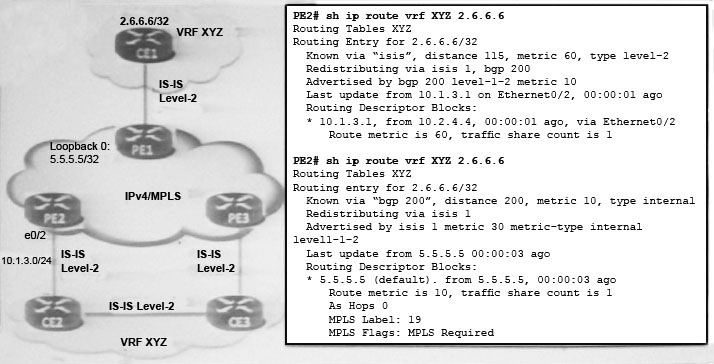
Refer to the exhibit. The 2.6.6.6/32 prefix is flapping when P1 is flapping. Which action can fix this issue?
- A. On PE2, allow only redistribution from BGP into IS-IS, on PE3, allow only redistribution from IS-IS into BGP.
- B. On PE2 and PE3, reconfigure redistribute BGP into IS-IS using the metric-type external parameter.
- C. Configure a sham link between PE2 and PE3.
- D. Configure all IS-IS instances as level-1-only.
Answer : B
Explanation:
Question 11
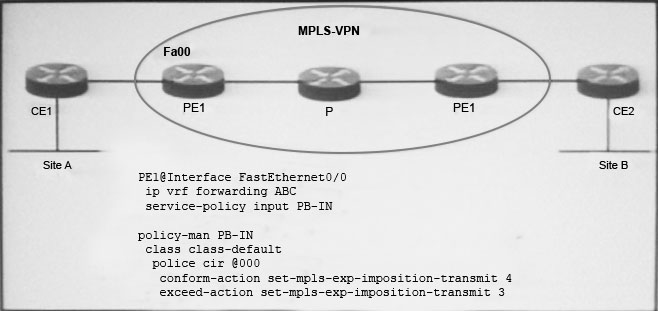
Refer to the exhibit. An MPLS Layer 3 VPN service has been provisioning for a customer. Which will be the ToS value at Site B for the exceeded traffic that is sent form Site A with ToS 2?
- A. 0
- B. 2
- C. 3
- D. 4
- E. No exceeded traffic will reach Site B.
Answer : C
Explanation:
Question 12

Refer to the exhibit. Customer ABC is peering with two service providers for Internet access. In order to prevent the AS 100 from becoming a transit AS between
ISP_1 and ISP_2, which BGP configuration must be applied to achieve this goal?
- A. CE1#CE2#ip as-path access-list 1 permit ^11$ip as-path access-list 1 permit ^$route-map LOCAL_ONLY permit 10route-map LOCAL_ONLY permit 10match as-path 1match as-path1router BGP 100router BGP 100neighbor 1.1.2.2 route-map LOCAL_ONLY outneighbor 1.1.1.2 route-map LOCAL_ONLY out
- B. CE1#CE2#ip as-path access-list 1 permit ^$ip as-path access-list 1 permit ^$route-map LOCAL_ONLY permit 10route-map LOCAL_ONLY permit 10match as- path 1match as-path 1router BGP 100router BGP 100neighbor 1.1.2.2 route-map LOCAL_ONLY outneighbor 1.1.1.2 route-map LOCAL_ONLY out
- C. CE1#CE2#ip as-path access-list1 permit ^100$ip as-path access-list 1 permit ^100$route-map LOCAL_ONLY permit 10route-map LOCAL_ONLY permit 10match as-path 1match as-path 1router BGP 100router BGP 100neighbor 1.1.2.2 route-map LOCAL_ONLY inneighbor1.1.1.2 route-map LOCAL_ONLY in
- D. CE1#CE2#ip as-path access-list 1 permit ^$ip as-path access-list 1 permit ^$route-map LOCAL_ONLY permit 10route-map LOCAL_ONLY permit 10match as- path 1match as-path 1router BGP 100router BGP 100neighbor 1.1.2.2 route-map LOCAL_ONLY inneighbor 1.1.1.2 route-map LOCAL_ONLY in
- E. CE1#CE2#ip as-path access-list 1 permit ^100$ip as-path access-list 1 permit ^100$route-map LOCAL_ONLY permit 10route-mapLOCAL_ONLY permit 10match as-path 1match as-path 1router BGP 100router BGP 100neighbor 1.1.2.2 route-map LOCAL_ONLY outneighbor 1.1.1.2 route-map LOCAL_ONLY out
Answer : B
Explanation:
Question 13

Refer to exhibit. Which conclusion is true?
- A. CT0 TE LSP can preempt CT1 TE. CT1 TE LSP cannot preempt CT0, except CT1 TE LSPs that corresponds to TE Class 0.
- B. CT0 TE LSP can preempt a CT1 TE LSP, but not vise versa. A CT1 TE LSP with a better priority can still preempt a CT1 TE LSP with worse priority.
- C. CT1 TE LSP can preempt some CT0 TE LSPs and vice versa however other TE LSPs cannot preempt CT1 TE LSPs that corresponds to TE Class 0.
- D. CT1 TE LSP can preempt a CT0 TE LSP, but not vice versa. A CT0 TE LSP with a better priority can still preempt a CT0 TE LSP with worse priority.
Answer : C
References:
Question 14
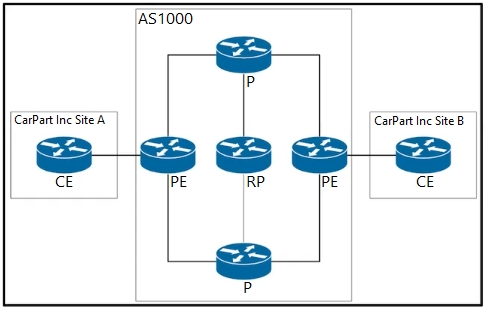
Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer has a requirement to enable MPLS TE tunnels on the network to be used by L3VPN customers. Which MPLS TE feature will allow the network engineer to configure MPLS TE LSPs by using a few CLI commands?
- A. AutoTunnel Mesh Groups on all PE routers
- B. AutoTunnel Mesh Groups on all P and PE routers
- C. AutoTunnel Primary and Backup on all P and PE routers
- D. AutoTunnel Primary and Backup on all P routers
Answer : A
Explanation:
Question 15
An MPLS network infrastructure of the service provider ABC is growing very quickly due to many recent acquisitions. Concerns arise about labeling each and every IP address on the service provider core network. The IP address pace is designed as per following:
-> Service provide ip address range is: 10.0.0.0/16
-> All loopbacks addresses use subnet mask /32
-> 10.0.0.0/24 range is used for loopback addresses
-> All other subnet masks used for links are /24 and /25
Which configuration does significantly reduce the label allocations without compromising LDP functionalities?
- A. ip prefix-list List1 deny 10.0.0.0/16le 20 ge 25!mpls ldp label allocate global prefix-list List1
- B. access-list 1 permit 10.0.0.0.0.0.255.255mpls ldp neighbor 10.0.0.1 labels accept 3
- C. mpls ldp password required for 10!access-list 10 permit 10.0.0.1access-list 10 permit 10.0.0.2access-list 10 permit 10.0.0.3
- D. mpls ldp label allocate global host-routes
Answer : D
Explanation: