CCNP Implementing Cisco IP Routing (ROUTE v2.0) v1.0
Question 1
A packet capture log indicates that several router solicitation messages were sent from a local host on the Ipv6 segment. What is the expected acknowledgment and its usage?
- A. Router acknowledgment messages will be forwarded upstream, where the DHCP server will allocate addresses to the local host.
- B. Routers on the Ipv6 segment will respond with an advertisement that provides an external path from the local subnet, as well as certain data, such as prefix discovery.
- C. Duplicate Address Detection will determine if any other local host is using the same Ipv6 address for communication with the Ipv6 routers on the segment.
- D. All local host traffic will be redirected to the router with the lowest ICMPv6 signature, which is statically defined by the network administrator.
Answer : B
Explanation:
Router Advertisements (RA) are sent in response to router solicitation messages. Router solicitation messages, which have a value of 133in the Type field of the
ICMP packet header, are sent by hosts at system startup so that the host can immediately autoconfigure without needing to wait for the next scheduled RA message. Given that router solicitation messages are usually sent by hosts at system startup (the host does not have a configured unicast address), the source address in router solicitation messages is usually the unspecified Ipv6 address (0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0). If the host has a configured unicast address, the unicast address of the interface sending the router solicitation message is used as the source address in the message. The destination address in router solicitation messages is the all-routers multicast address with a scope of the link. When an RA is sent in response to a router solicitation, the destination address in the RA message is the unicast address of the source of the router solicitation message.
RA messages typically include the following information:
"¢ One or more on link Ipv6 prefixes that nodes on the local link can use to automatically configure their Ipv6 addresses "¢ Lifetime information for each prefix included in the advertisement "¢ Sets of flags that indicate the type of autoconfiguration (stateless or stateful) that can be completed "¢ Default router information (whether the router sending the advertisement should be used as a default router and, if so, the amount of time (in seconds) the router should be used as a default router) "¢ Additional information for hosts, such as the hop limit and MTU a host should use in packets that it originates
Question 2
SIMULATION -
Route.com is a small IT corporation that is attempting to implement the network shown in the exhibit. Currently the implementation is partially completed. OSPF has been configured on routers
Chicago and NewYork. The SO/O interface on Chicago and the SO/1 interface on NewYork are in
Area 0. The loopbackO interface on NewYork is in Area 1. However, they cannot ping from the serial interface of the Seattle router to the loopback interface of the NewYork router. You have been asked to complete the implementation to allow this ping.
ROUTE.com"™s corporate implementation guidelines require:
"¢ The OSPF process ID for all routers must be 10.
"¢ The routing protocol for each interface must be enabled under the routing process. "¢ The routing protocol must be enabled for each interface using the most specific wildcard mask possible. "¢ The serial link between Seattle and Chicago must be in OSPF area 21. "¢ OSPF area 21 must not receive any inter-area or external routes.
Network Information -
Seattle -
S0/0 192.168.16.5/30 "" Link between Seattle and Chicago
Secret Password: cisco -
Chicago -
S0/0 192.168.54.9/30 "" Link between Chicago and New York
S0/1 192.168.16.6/30 "" Link between Seattle and Chicago
Secret Password: cisco -
New York -
S0/1 192.168.54.10/30 "" Link between Chicago and New York
Loopback0 172.16.189.189 -
Secret Password: cisco -
Answer : See explanation below
Explanation:
Note: In actual exam, the IP addressing, OSPF areas and process ID, and router hostnames may change, but the overall solution is the same.
Seattle"™s S0/0 IP Address is 192.168.16.5/30. So, we need to find the network address and wildcard mask of 192.168.16.5/30 in order to configure the OSPF.
IP Address: 192.168.16.5 /30 -
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.252 -
Here subtract 252 from 2565, 256-252 = 4, hence the subnets will increment by 4.
First, find the 4thoctet of the Network Address:

The 4thoctet of IP address (192.168.16.5) belongs to subnet 1 (4 to 7).
Network Address: 192.168.16.4 -
Broadcast Address: 192.168.16.7 -
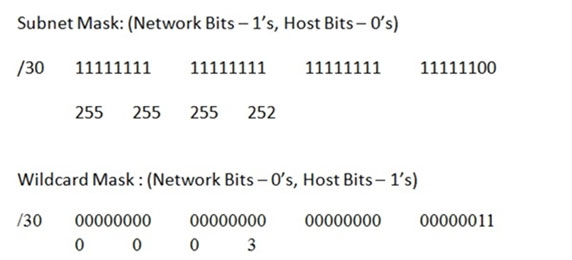
Let"™s find the wildcard mask of /30.
Subnet Mask: (Network Bits "" 1"™s, Host Bits "" 0"™s)
Let"™s find the wildcard mask of /30:
Now we configure OSPF using process ID 10 (note the process ID may change to something else in real exam).
Seattle>enable -
Password:
Seattle#conf t -
Seattle(config)#router ospf 10 -
Seattle(config-router)#network 192.168.16.4 0.0.0.3 area 21
One of the tasks states that area 21 should not receive any external or inter-area routes (except the default route).
Seattle(config-router)#area 21 stub
Seattle(config-router)#end -
Seattle#copy run start -
Chicago Configuration:
Chicago>enable -
Password: cisco -
Chicago#conf t -
Chicago(config)#router ospf10 -
We need to add Chicago"™s S0/1 interface to Area 21
Chicago(config-router)#network 192.168.16.4 0.0.0.3 area 21
Again, area 21 should not receive any external or inter-area routes (except the default route).
In order to accomplish this, we must stop LSA Type 5 if we don"™t want to send external routes. And if we don"™t want to send inter-area routes, we have to stop LSA
Type 3 and Type 4. There fore we want to configure area 21 as a totally stubby area.
Chicago(config-router)#area 21 stub no-summary
Chicago(config-router)#end -
Chicago#copy run start -
The other interface on the Chicago router is already configured correctly in this scenario, as well as the New York router so there is nothing that needs to be done on that router.
Question 3
SIMULATION -
JS Industries has expanded their business with the addition of their first remote office. The remote office router (R3) was previously configured and all corporate subnets were reachable from R3. JS Industries is interested in using route summarization along with the EIGRP Stub Routing feature to increase network stability while reducing the memory usage and bandwidth utilization to R3. Another network professional was tasked with implementing this solution. However, in the process of configuring EIGRP stub routing connectivity with the remote network devices off of R3 has been lost.
Currently EIGRP is configured on all routers R2, R3, and R4 in the network. Your task is to identify and resolve the cause of connectivity failure with the remote office router R3. Once the issue has been resolved you should complete the task by configuring route summarization only to the remote office router R3.
You have corrected the fault when pings from R2 to the R3 LAN interface are successful, and the R3 IP routing table only contains 2 10.0.0.0 subnets.
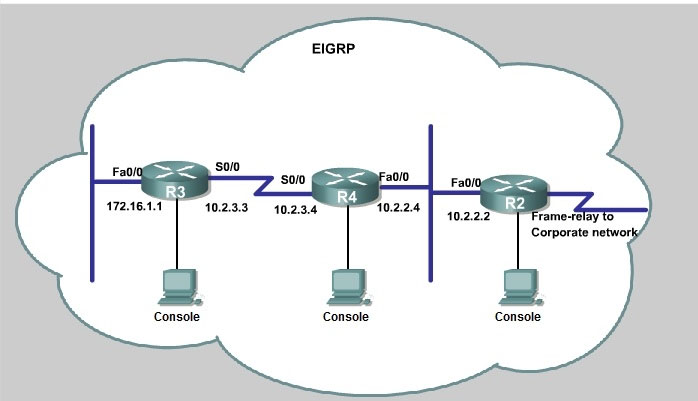
Answer : See explanation below
Explanation:
First we have to figure out why R3 and R4 can not communicate with each other. Use the show running-config command on router R3.
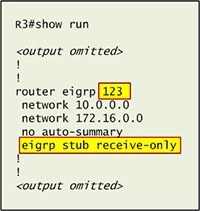
Notice that R3 is configured as a stub receive-only router. The receive-only keyword will restrict the router from sharing any of its routes with any other router in that EIGRP autonomous system. This keyword will also prevent any type of route from being sent. Therefore we will remove this command and replace it with the eigrp stub command:
R3# configure terminal R3(config)# router eigrp 123 R3(config-router)# no eigrp stub receive-only R3(config-router)# eigrp stub
R3(config-router)# end -
Now R3 will send updates containing its connected and summary routes to other routers. Notice that the eigrp stub command equals to the eigrp stub connected summary because the connected and summary options are enabled by default.
Next we will configure router R3 so that it has only 2 subnets of 10.0.0.0 network. Use the show ip route command on R3 to view its routing table:
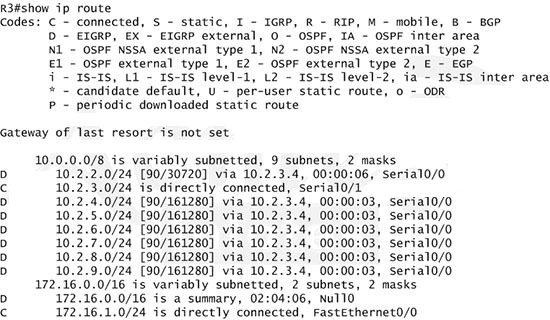
Because we want the routing table of R3 only have 2 subnets so we have to summary sub-networks at the interface which is connected with R3, the s0/0 interface of R4.
There is one interesting thing about the output of the show ip route shown above: the 10.2.3.0/24, which is a directly connected network of R3. We can"™t get rid of it in the routing table no matter what technique we use to summary the networks. Therefore, to make the routing table of R3 has only 2 subnets we have to summary other subnets into one subnet.
In the output if we don"™t see the summary line (like 10.0.0.0/8 is a summary"¦) then we should use the command ip summary-address eigrp 123 10.2.0.0
255.255.0.0 so that all the ping can work well.
In conclusion, we will use the ip summary-address eigrp 123 10.2.0.0 255.255.0.0 at the interface s0/0 of R4 to summary.
R4> enable R4# conf t -
R4(config)# interface s0/0 R4(config-if)# ip summary-address eigrp 123 10.2.0.0 255.255.0.0
Now we jump back to R3 and use the show ip route command to verify the effect, the output is shown below:
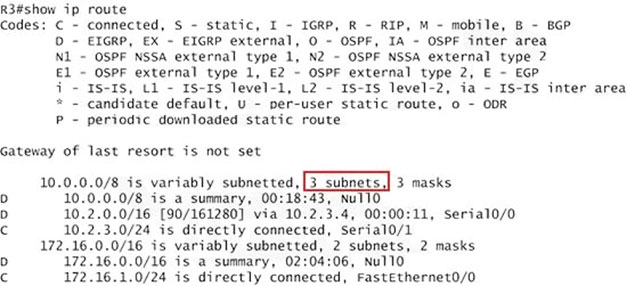
Note: Please notice that the IP addresses and the subnet masks in your real exam might be different so you might use different ones to solve this question.
Just for your information, notice that if you use another network than 10.0.0.0/8 to summary, for example, if you use the command ip summary-address eigrp 123
10.2.0.0 255.255.0.0 you will leave a /16 network in the output of the show ip route command.
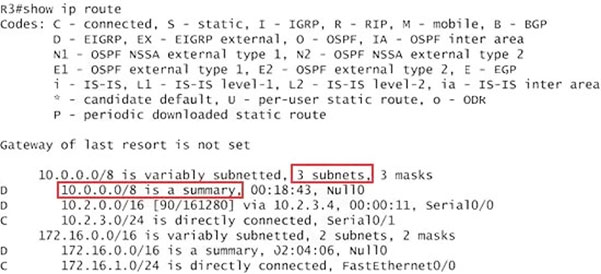
But in your real exam, if you don"™t see the line "10.0.0.0/8 is a summary, Null0" then you can summarize using the network 10.2.0.0/16. This summarization is better because all the pings can work well.
Finally don"™t forget to use the copy run start command on routers R3 and R4 to save the configurations.
R3(config-if)# end -
R3# copy run start -
R4(config-i
Question 4
SIMULATION -
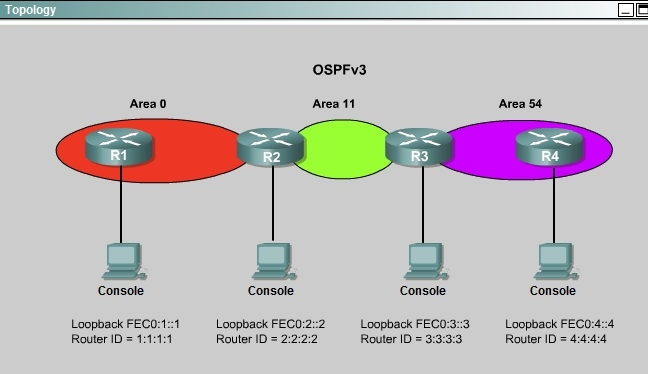
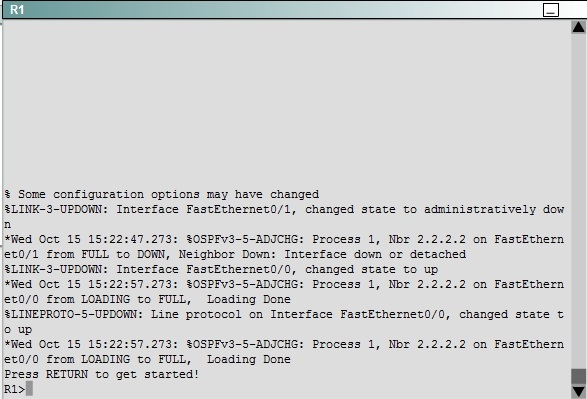
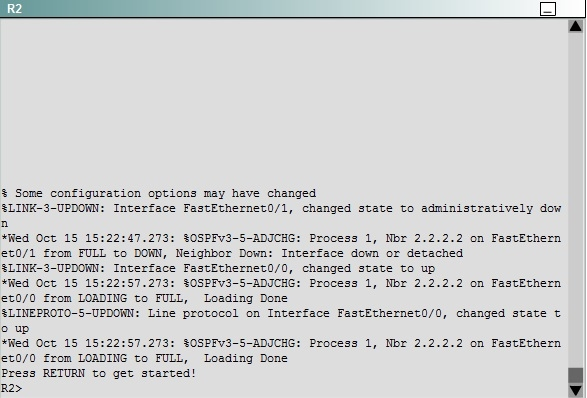
ROUTE.com is a small IT corporation that has an existing enterprise network that is running Ipv6 0SPFv3. Currently OSPF is configured on all routers. However,
R4"™s loopback address (FEC0:4:4) cannot be seen in R1"™s Ipv6 routing table. You are tasked with identifying the cause of this fault and implementing the needed corrective actions that uses OPSF features and does not change the current area assignments. You will know that you have corrected the fault when R4"™s loopback address (FEC0:4:4) can be seen in RTs Ipv6 routing table.
Special Note: To gain the maximum number of points you must remove all incorrect or unneeded configuration statements related to this issue.
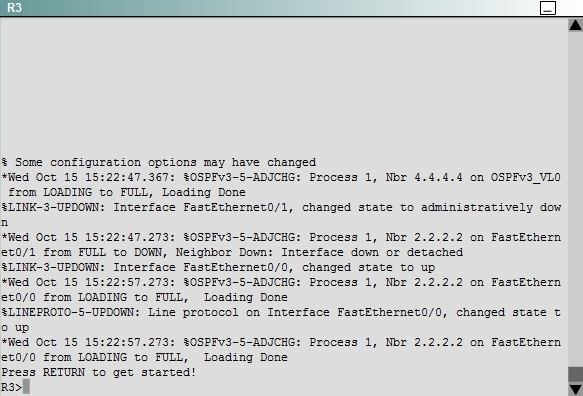
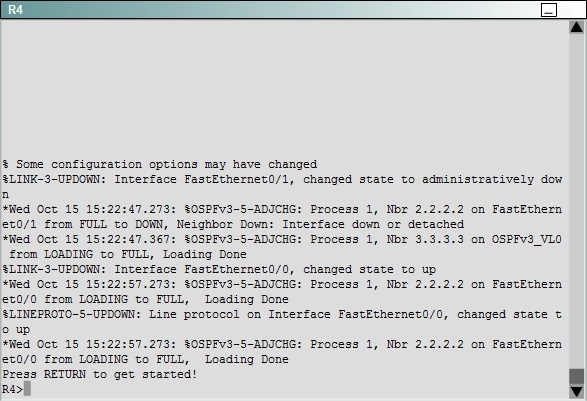
Answer : See explanation below
Explanation:
To troubleshoot the problem, first issue the show running-config on all of 4 routers. Pay more attention to the outputs of routers R2 and R3 The output of the "show running-config" command of R2:

The output of the "show running-config" command of R3:
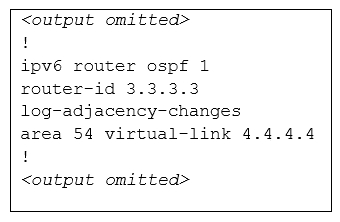
We knew that all areas in an Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) autonomous system must be physically connected to the backbone area (Area 0). In some cases, where this is not possible, we can use a virtual link to connect to the backbone through a non-backbone area. The area through which you configure the virtual link is known as a transit area. In this case, the area 11 will become the transit area. Therefore, routers R2 and R3 must be configured with the area <area id> virtual- link <neighbor router-id>command. + Configure virtual link on R2 (from the first output above, we learned that the OSPF process ID of R2 is 1):
R2>enable -
R2#configure terminal -
R2(config)#ipv6 router ospf 1 -
R2(config-rtr)#area 11 virtual-link 3.3.3.3
Save the configuration:
R2(config-rtr)#end -
R2#copy running-config startup-config
(Notice that we have to use neighbor router-id 3.3.3.3, not R2"™s router-id 2.2.2.2) + Configure virtual link on R3 (from the second output above, we learned that the
OSPF process ID of R3 is 1 and we have to disable the wrong configuration of "area 54 virtual-link 4.4.4.4"):
R3>enable -
R3#configure terminal -
R3(config)#ipv6 router ospf 1 -
R3(config-rtr)#no area 54 virtual-link 4.4.4.4
R3(config-rtr)#area 11 virtual-link 2.2.2.2
Save the configuration:
R3(config-rtr)#end -
R3#copy running-config startup-config
You should check the configuration of R4, too. Make sure to remove the incorrect configuration statements to get the full points.
R4(config)#ipv6 router ospf 1 -
R4(config-router)#no area 54 virtual-link 3.3.3.3
R4(config-router)#end -
After finishing the configuration doesn"™t forget to ping between R1 and R4 to make sure they work.
Note. If you want to check the routing information, use the show ipv6 route command, not "show ip route".
Question 5
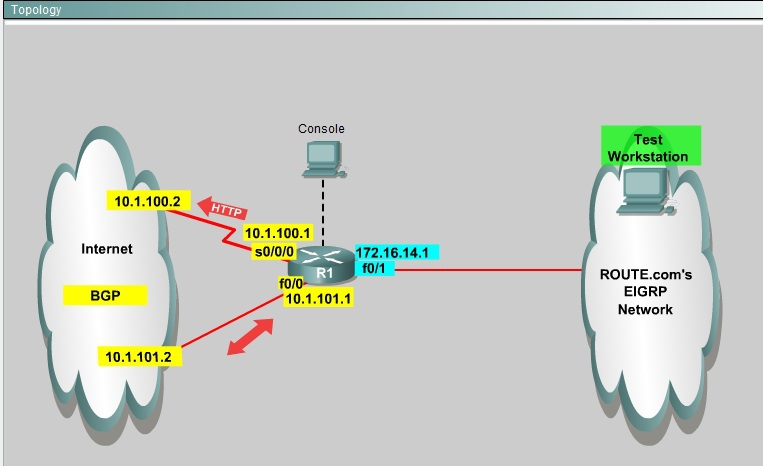
SIMULATION -
You are a network engineer with ROUTE.com, a small IT company. ROUTE.com has two connections to the Internet; one via a frame relay link and one via an
EoMPLS link. IT policy requires that all outbound HTTP traffic use the frame relay link when it is available. All other traffic may use either link. No static or default routing is allowed.
Choose and configure the appropriate path selection feature to accomplish this task. You may use the Test Workstation to generate HTTP traffic to validate your solution.
Answer : See explanation below
Explanation:
First you need to configure access list to HTTP traffic and then configure that access list. After that configure the route map and then apply it on the interface to the server in EIGRP network.
Question 6
SIMULATION -
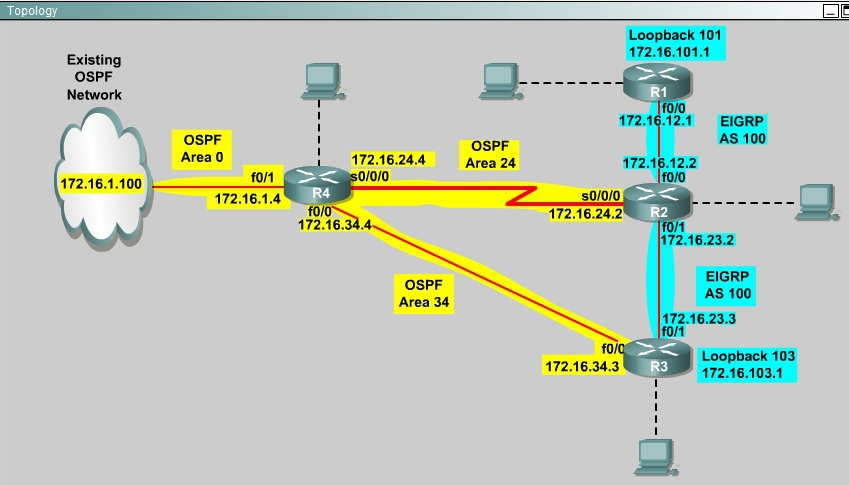
You are a network engineer with ROUTE.com, a small IT company. They have recently merged two organizations and now need to merge their networks as shown in the topology exhibit. One network is using OSPF as its IGP and the other is using EIGRP as its IGP. R4 has been added to the existing OSPF network to provide the interconnect between the OSPF and EIGRP networks. Two links have been added that will provide redundancy.
The network requirements state that you must be able to ping and telnet from loopback 101 on R1 to the OPSF domain test address of 172.16.1.100. All traffic must use the shortest path that provides the greatest bandwidth. The redundant paths from the OSPF network to the EIGRP network must be available in case of a link failure. No static or default routing is allowed in either network.
A previous network engineer has started the merger implementation and has successfully assigned and verified all IP addressing and basic IGP routing. You have been tasked with completing the implementation and ensuring that the network requirements are met. You may not remove or change any of the configuration commands currently on any of the routers. You may add new commands or change default values.
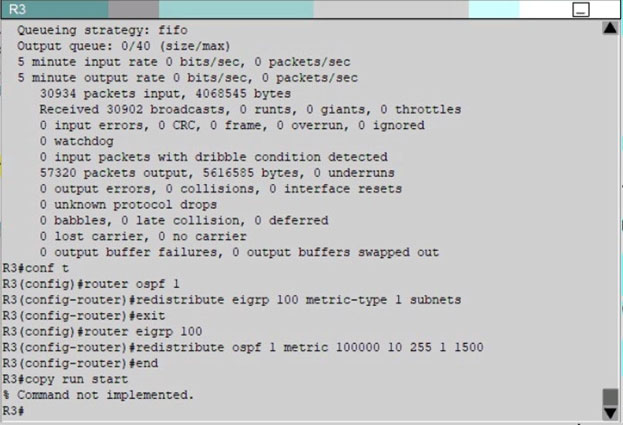
Answer : Please see explanation
Explanation:
First we need to find out 5 parameters (Bandwidth, Delay, Reliability, Load, MTU) of the s0/0/0 interface (the interface of R2 connected to R4) for redistribution:
R2#show interface s0/0/0 -
Write down these 5 parameters, notice that we have to divide the Delay by 10 because the metric unit is in tens of microsecond. For example, we get
Bandwidth=1544 Kbit, Delay=20000 us, Reliability=255, Load=1, MTU=1500 bytes then we would redistribute as follows:
R2#config terminal -
R2(config)# router ospf 1 -
R2(config-router)# redistribute eigrp 100 metric-type 1 subnets
R2(config-router)#exit -
R2(config-router)#router eigrp 100
R2(config-router)#redistribute ospf 1 metric 1544 2000 255 1 1500
Note: In fact, these parameters are just used for reference and we can use other parameters with no problem.
If the delay is 20000us then we need to divide it by 10, that is 20000 / 10 = 2000)
For R3 we use the show interface fa0/0 to get 5 parameters too
R3#show interface fa0/0 -
For example we get Bandwidth=10000 Kbit, Delay=1000 us, Reliability=255, Load=1, MTU=1500 bytes
R3#config terminal -
R3(config)#router ospf 1 -
R3(config-router)#redistribute eigrp 100 metric-type 1 subnets
R3(config)#exit -
R3(config-router)#router eigrp 100
R3(config-router)#redistribute ospf 1 metric 10000 100 255 1 1500
Finally you should try to "show ip route" to see the 172.16.100.1 network (the network behind R4) in the routing table of R1 and make a ping from R1 to this network.
Note: If the link between R2 and R3 is FastEthernet link, we must put the command below under EIGRP process to make traffic from R1 to go through R3 (R1 ->
R2 -> R3 -> R4), which is better than R1 -> R2 -> R4.
R2(config-router)# distance eigrp 90 105
This command sets the Administrative Distance of all EIGRP internal routes to 90 and all EIGRP external routes to 105, which is smaller than the Administrative
Distance of OSPF (110) -> the link between R2 & R3 will be preferred to the serial link between R2 & R4.
Note: The actual OPSF and EIGRP process numbers may change in the actual exam so be sure to use the actual correct values, but the overall solution is the same.
Question 7
Scenario -
You have been asked to evaluate how EIGRP is functioning in a customer network. Access the device consoles to answer the questions.
Instructions -
- Enter IOS commands on the device to verify network operation and answer for multiple-choice questions.
- THIS TASK DOES NOT REQUIRE DEVICE CONFIGURATION.
- Click on the individual device icons or use the tab at the bottom of the screen to gain access to the console for each device.
- No console or enable passwords are required.
- To access the multiple-choice questions, click on the numbered boxes on the left of the top panel.
- There are five multiple-choice questions with this task. Be sure to answer all five questions before selecting the Next button.

What percent of R1"™s interfaces bandwidth is EIGRP allowed to use?
- A. 10
- B. 20
- C. 30
- D. 40
Answer : B

Question 8
Scenario -
You have been asked to evaluate an OSPF network setup in a test lab and to answer questions a customer has about its operation. The customer has disabled your access to the show running-config command.
Instructions -
- Enter IOS commands on the device to verify network operation and answer for multiple-choice questions.
- THIS TASK DOES NOT REQUIRE DEVICE CONFIGURATION.
- Click on the icon or the lab at the bottom of the screen to gain access to the console for each device.
- No console or enable passwords are required.
- To access the multiple-choice questions, click on the numbered boxes on the left of the top panel.
- There are four multiple-choice questions with this task. Be sure to answer all four questions before selecting the Next button.
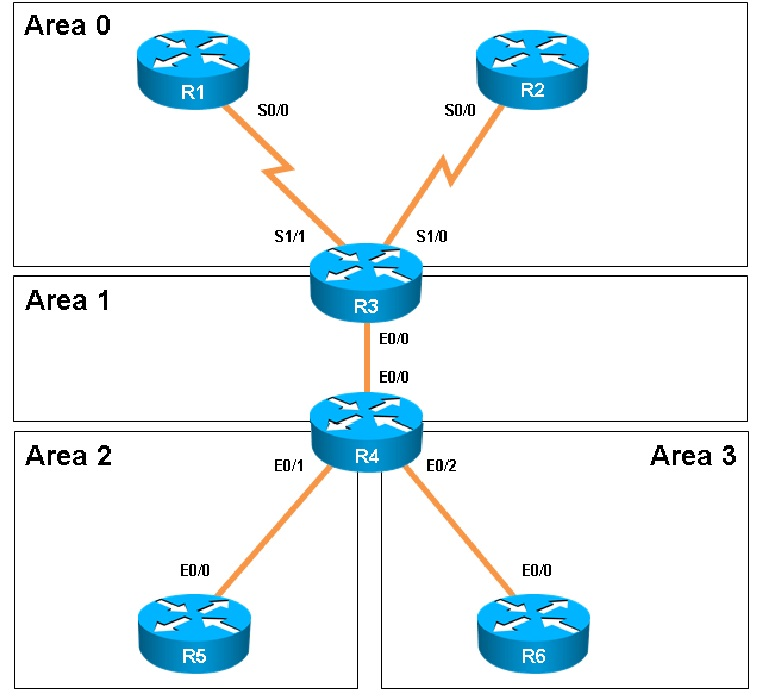

How old is the Type 4 LSA from Router 3 for area 1 on the router R5, based on the output you have examined?
- A. 1858
- B. 1601
- C. 600
- D. 1569
Answer : A
Explanation:
Part of the "show ip ospf topology" command on R5 shows this:
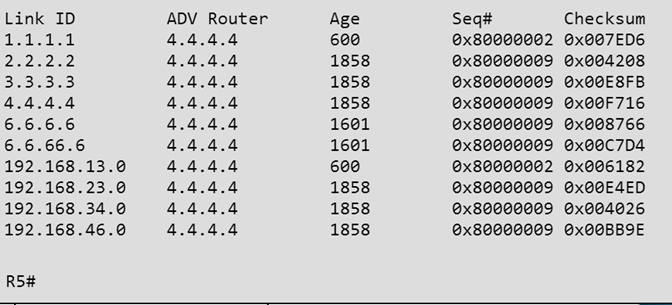
The Link ID of R3 (3.3.3.3) shows the age is 1858.
Question 9
Scenario -
You have been asked to evaluate an OSPF network setup in a test lab and to answer questions a customer has about its operation. The customer has disabled your access to the show running-config command.
Instructions -
- Enter IOS commands on the device to verify network operation and answer for multiple-choice questions.
- THIS TASK DOES NOT REQUIRE DEVICE CONFIGURATION.
- Click on the icon or the lab at the bottom of the screen to gain access to the console for each device.
- No console or enable passwords are required.
- To access the multiple-choice questions, click on the numbered boxes on the left of the top panel.
- There are four multiple-choice questions with this task. Be sure to answer all four questions before selecting the Next button.

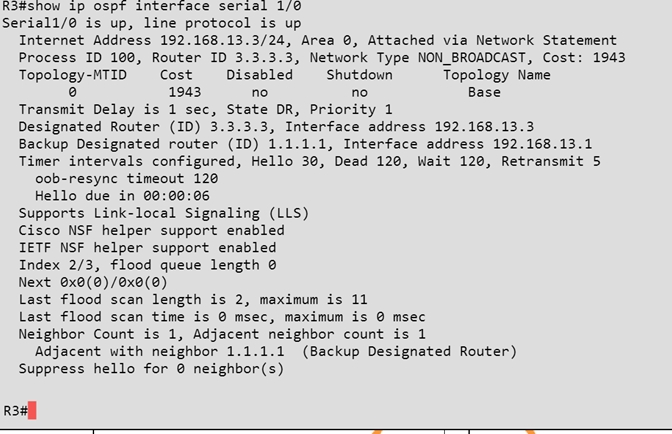
Which of the following statements is true about the serial links that terminate in R3?
- A. The R1-R3 link needs the neighbor command for the adjacency to stay up
- B. The R2-R3 link OSPF timer values are 30, 120, 120
- C. The R1-R3 link OSPF timer values should be 10, 40, 40
- D. R3 is responsible for flooding LSUs to all the routers on the network
Answer : B
Explanation:
We can see the configured timers using the following command:
Question 10
Scenario -
You have been asked to evaluate an OSPF network setup in a test lab and to answer questions a customer has about its operation. The customer has disabled your access to the show running-config command.
Instructions -
- Enter IOS commands on the device to verify network operation and answer for multiple-choice questions.
- THIS TASK DOES NOT REQUIRE DEVICE CONFIGURATION.
- Click on the icon or the lab at the bottom of the screen to gain access to the console for each device.
- No console or enable passwords are required.
- To access the multiple-choice questions, click on the numbered boxes on the left of the top panel.
- There are four multiple-choice questions with this task. Be sure to answer all four questions before selecting the Next button.

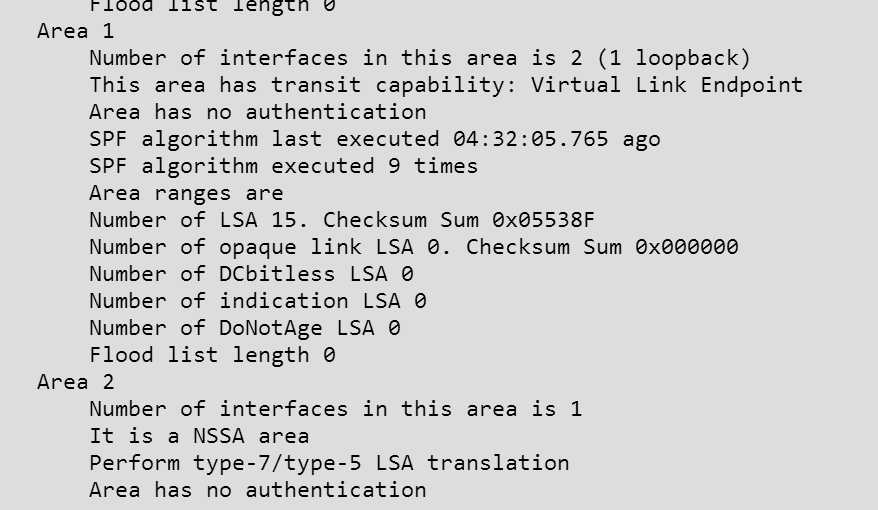
How many times was SPF algorithm executed on R4 for Area 1?
- A. 1
- B. 5
- C. 9
- D. 20
- E. 54
- F. 224
Answer : C
Explanation:
This can be found using the "show ip ospf" command on R4. Look for the Area 1 stats which shows this:
Question 11
Scenario -
You have been asked to evaluate an OSPF network setup in a test lab and to answer questions a customer has about its operation. The customer has disabled your access to the show running-config command.
Instructions -
- Enter IOS commands on the device to verify network operation and answer for multiple-choice questions.
- THIS TASK DOES NOT REQUIRE DEVICE CONFIGURATION.
- Click on the icon or the lab at the bottom of the screen to gain access to the console for each device.
- No console or enable passwords are required.
- To access the multiple-choice questions, click on the numbered boxes on the left of the top panel.
- There are four multiple-choice questions with this task. Be sure to answer all four questions before selecting the Next button.
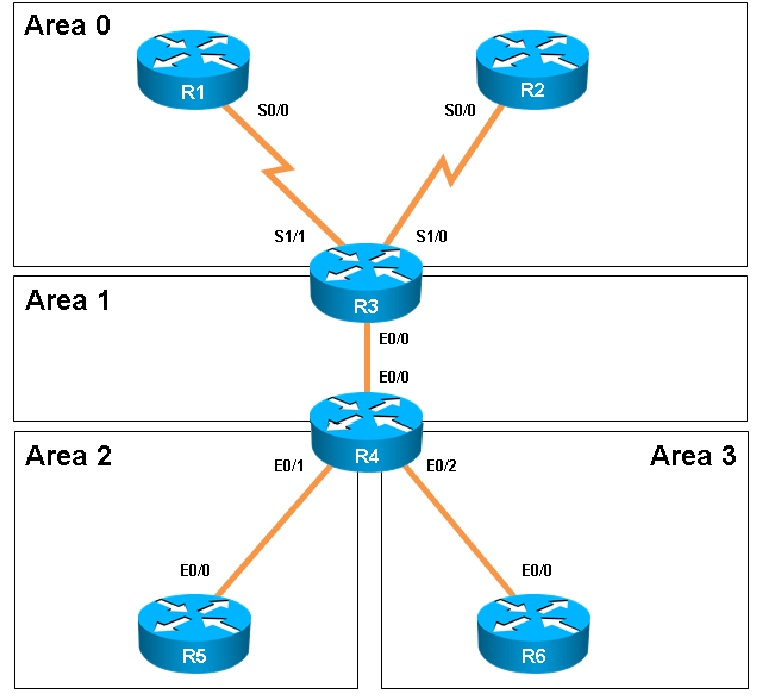

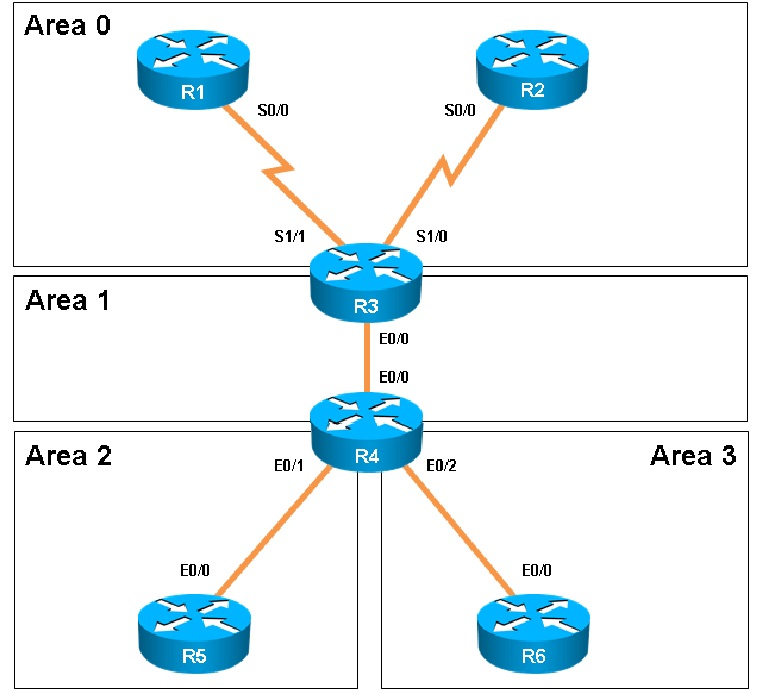
Areas of Router 5 and 6 are not normal areas. Inspect their routing tables and determine which statement is true.
- A. R5"™s Loopback and R6"™s Loopback are both present in R5"™s Routing table
- B. R5"™s Loopback and R6"™s Loopback are both present in R6"™s Routing table
- C. Only R5"™s loopback is present in R5"™s Routing table
- D. Only R6"™s loopback is present in R5"™s Routing table
- E. Only R5"™s loopback is present in R6"™s Routing table
Answer : A
Explanation:
Here are the routing tables of R5 and R6:
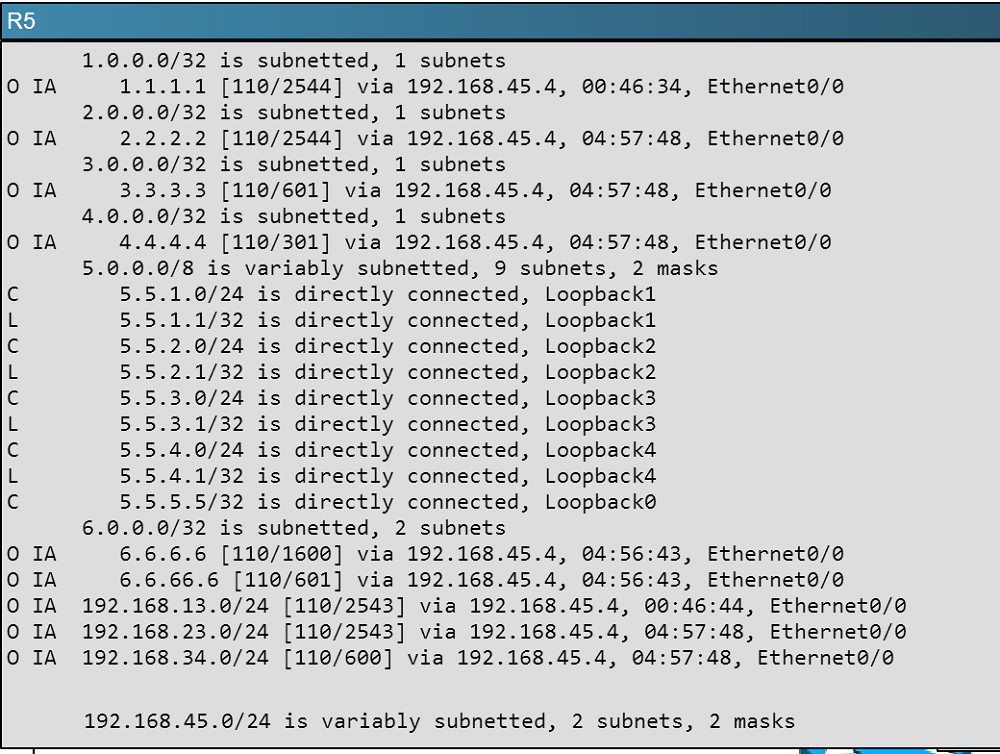
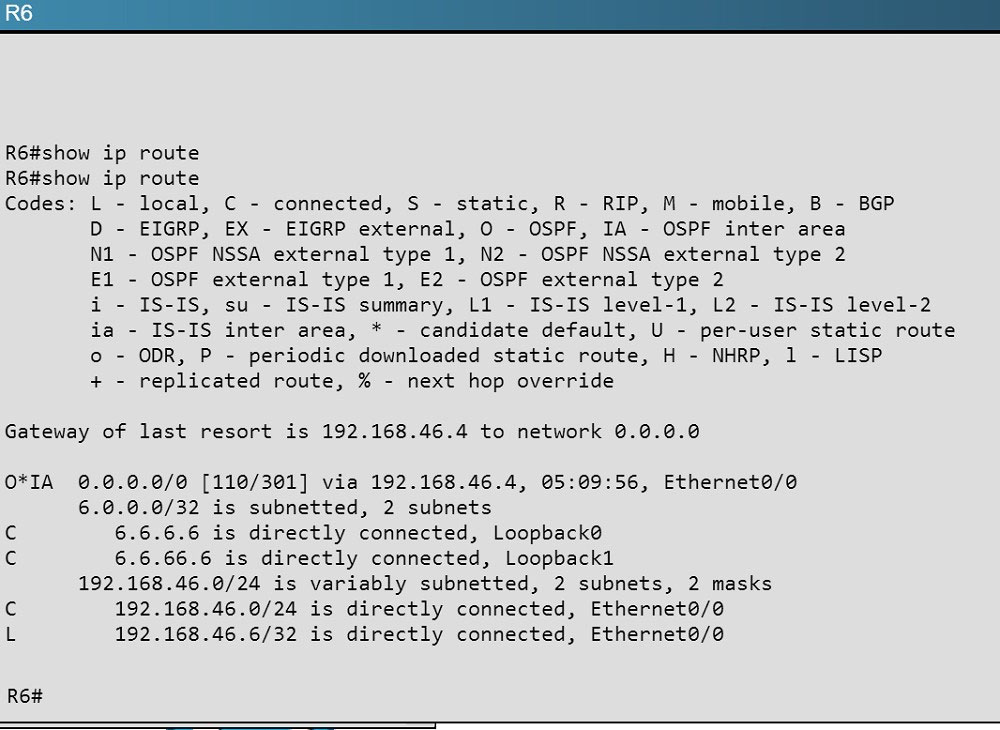
Here we see R5"™s loopbacks in the routing table shown as connected, and the 6.6.6.6 loopback IP address of R6 is also seen as an OSPF route in R5"™s routing table.
Question 12
A network engineer is migrating an IPv4 point-to multipoint Frame Relay network to IPv6. Which IPv6 address type must be used in a Frame Relay map configuration command to ensure that the OSPF protocol still works after migration?
- A. unique-local
- B. link-local
- C. global
- D. site-local
- E. multicast
Answer : B
Question 13
A network engineer replaced a bad router with a spare, used router in an OSPF network. After the replacement, OSPF neighborship is not being established on one of the interfaces. Which two reasons cause this issue? (Choose two.)
- A. authentication mismatch
- B. MTU mismatch
- C. OSPF timers match
- D. OSPF process numbers do not match on both neighbor routers.
- E. area numbers match
Answer : AC
Question 14
By default, what is the maximum number of equal-metric paths that BGP uses for load balancing?
- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 4
- D. 6
Answer : A
Explanation:
By default, BGP chooses one best path among the possible equal-cost paths that are learned from one AS. However, you can change the maximum number of parallel equal-cost paths that are allowed. In order to make this change, include the maximum-paths paths command under the BGP configuration. Use a number between 1 and 6 for the paths argument.
Question 15
Which feature is not supported when fast-switched PBR is in use?
- A. the set ip default next-hop command
- B. the set ip next-hop interface command
- C. matching IP addresses to a named ACL
- D. matching IP addresses to a prefix list
Answer : A
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/iproute_pi/configuration/xe-3se/3850/iri-xe-3se-3850-book/iri-fast-switched-policy-rtg.pdf